The advent of laser engraving technology has transformed the creation of detailed designs and patterns on stone and other sturdy materials. This guide will help you understand how laser engraving machines operate, their advantages, and their importance in the engraving sector for professionals and hobbyists. This article elevates the discussion on laser engraving machines to the level of precision and techniques necessary to engrave artwork, custom stone signage, and other personal touches quickly and easily. We will also examine the most important factors to remember when selecting an appropriate machine to achieve the best results on every project.
What is a laser engraving machine for stone and how does it work?

A laser engraving machine for stone is a powerful and specialized tool that utilizes a high-intensity beam of light to etch intricate patterns, text, or designs on stone surfaces. This process involves applying a powerful light beam, a laser, to the stone. The heat from the laser vaporizes the surface material and leaves a permanent mark. The machines have advanced yet simple software controls that allow the marking to be done precisely and consistently. Therefore, these machines are widely used for everything from ornamental decoration to industrial-grade labeling.
Understanding laser technology for stone engraving
Stone laser engraving uses three primary components: the software interface, motion control system, and laser source. The source of the laser is typically a CO2 or fiber laser which produces the beam used in the engraving. While CO2 lasers are effective for natural stones such as granite and marble, fiber lasers are more effective for specific engineered stones. The motion control system determines the positioning and movement of the stone or laser, allowing for variations in the designs and their detail. Users can upload or design an image, modify the power and speed, and set the alignment to achieve the best achievable output through interface software.
In laser engraving, the first step involves the software interpreting the design into powers that will be utilized and how deep the engraving will go. Upon contact with the stone, the laser beam emits engraves by transforming energy into heat and vaporizing or melting particles. Since the engraving is non-contact, the stone’s integrity is maintained without damage even if highly detailed engravings are done on it. Modern machines are outfitted with cooling and safety features to improve performance and protect the material from damage. The adaptability and precision of these machines make them essential in various industries, including architecture, memorial art, and custom product design.
Types of lasers used for stone engraving: CO2, fiber, and diode
The three primary types of stone engraving are diode, fiber, and CO2 lasers. Since CO2 lasers are powerful, they can engrave soft stones of many types, such as marble, granite, and other stone patterns. Likewise, Fiber lasers can engrave with a much deeper cavity onto more complex materials due to their superior level of precision and efficiency. Lastly, Diode lasers allow for less power but are much more affordable, making them more efficient when working on softer stone and detail-oriented projects. Each type covers a specific range of materials and project requirements, ensuring the appropriate approach achieves an optimal result.
The process of laser engraving on stone surfaces
The design produced on the stone surface is permanent and precise due to the high-powered laser beam projecting an image onto the stone’s surface. The initial step involves picking out a laser type, like CO2 or fiber, after accessing the stone’s strength and the project’s requirement. The stone’s surface also requires proper preparation, including cleaning it to remove debris or polishing it to ensure smooth engraving.
The laser engraving process begins with the creation of engraving designs, which can be in vector or raster formats, albeit with a few variations. This is saved and set up using the laser software. After this setup, the laser engraving machine will focus its energy on the stone and vaporize the surface layer into the desired design. The laser’s power, frequency, and speed need to be calibrated according to the type and density of the stone, as these parameters radically change the depth and clarity of the engraving.
Commonly engraved stones include granite, marble, and slate, as each reacts differently with the applied laser. The laser creates a lighter frosted effect for granite, while marble displays sharp contrasts. Water cooling systems are also applied in these processes to withstand high temperatures and eliminate any excess heat that may damage the surrounding material. After engraving, cleaning the stone with a solvent or brush is often necessary to make the design more visible. Achieving mastery in this intricate workflow guarantees high precision and durability in the finished product.
Which types of stone can be engraved with a laser machine?

Granite, marble, slate, and basalt are among the stone types that can be engraved using the laser machine. Softer stones like limestone and sandstone can also be engraved, though their porosity may require setting changes on the laser. Every type of stone possesses a unique way of reacting with a laser, which determines its final shape, elevating the process’s importance for the stone type.
Granite, marble, and slate: Popular choices for laser engraving
Granite, marble, and slate are popular selections for engraving due to their strength, beauty, and ease of engraving with precision. Due to the sharp and solid granite surface, it is suitable for the detailed and enduring engraving required in monuments and plaques. It is also great for memorials or plaques that are permanently installed. Marble is smooth and elegant, which helps to create intricate designs, though it has some variation depending on its natural composition. Slate has a rustic look. Its delicate structure can hold a lot of detail and is suitable for delicate ornaments like signs and coasters. To achieve the best results, the correct settings on the laser need to be adjusted for each design by considering the stone’s power, speed, and texture.
Natural stones vs. engineered stones for laser engraving
Whether to use natural or engineered stones when laser engraving would depend on the application since both have their strengths and weaknesses; for example, granite or marble has remarkable textures and grain formations, which add more value to the well-crafted engraving design. However, the inconsistency in their composition makes it harder to use them because the laser settings need to be adjusted frequently. On the contrary, while engineered stones do not have the same charm as natural stones, they are more uniform in structure. Hence, more reliable performance can be expected during engraving. Using them can lead to greater control and consistency. Ultimately, it all concerns whether one values aesthetic distinctiveness or reliable performance.
Exploring unique stone materials: Basalt, sandstone, and pebbles
Each stone material, such as basalt, sandstone, and pebbles, has distinguishable features. The strength and density of concrete make it fabulous for section engravings; that’s why interlocking blocks with fine-grained structures are preferred. Sandstone is excellent for rustic textured finishes because of its shallow natural layering and softness, yet it is brittle, so care must be observed during usage. Lastly, abstracted pebbles from nature have fantastic, unique, carvable textures and shapes that make them perfect for small engraving projects. Beholding the shapes and sizes of pebbles poses some challenges. Therefore, they can be difficult to work with due to their textures and shapes. Ultimately, each material has its own aesthetic and functional objectives that must be observed when working on the project.
What are the key features to look for in a stone laser engraving machine?

Buying a stone laser engraving machine is like grasping the ropes of the instrument. Essential features include output power, precision, and the machine’s durability. High-powered lasers ensure clean and deep etching while simultaneously engraving dense materials like stone. To accomplish intricate designs and detailed patterns, precision is needed. Compatibility with various rocks, flexible software for design editing, and the ease of maintenance and cooling systems are additional factors that should be evaluated carefully. Lastly, the machine’s durability is critical as it needs to withstand the wear and tear of hard surface engraving.
Laser power and working area considerations
It is crucial to the application in question that the output parameters match those needed. An output of 100W is a baseline when executing engraving work on dense materials such as granite or marble to ensure more precise and deeper cuts. Lower-powered lasers may handle softer stones or surface-level etchings, but intricate designs or hefty workloads may be challenging. The machine’s working area should be proportional to the size of the materials you intend to engrave. For bulk operations, larger slabs of stone might necessitate a working area of 24” x 36” or even larger. Smaller areas benefit compact or detailed work, while precision may suffer over large slabs. Optimal systems offer adjustable area settings to tackle problems involving project scales.
Engraving speed and precision capabilities
The engravings’ speed and precision are critical to assessing the engraving machine’s performance. Speed metrics are given in millimeters per second (mm/s) or inches per second (ips), defining how fast a design can be completed on the machine. High-speed machines ranging from 500 mm/s to 1000 mm/s are more amenable for time-sensitive or large-scale projects. However, with increased speed comes the loss of precision while working on delicate materials or intricate designs.
Precision, on the other hand, depends on the accuracy of the machine, often referred to as its resolution. For example, precision is often referred to using dots per inch (DPI) and minimum achievable line width when considering a laser engraving machine. When deep engraving is to be achieved, machines with resolutions of 1000 DPI or greater are needed. Advanced systems can enhance precision by incorporating automatic focus setup, stabilized laser beams, and motion control systems to maintain accuracy while performing tasks requiring speed. Most professional machines allow users to control the balance between speed and accuracy, resulting in effortless changes between modes depending on the project.
Software compatibility and ease of use
As with any professional laser engraving machine, the models under consideration must help their users not only engrave but also quickly transfer design files into the machine. This, together with the ability to use Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, AutoCAD, or CAD files, is critical for modern systems. Professional engraving machines with proprietary software do ensure some level of workflow streamlining. However, effortless importing of standard file formats.SVG.DXF, .PDF, and other file types are mandatory. The process is made even easier with user-friendly interfaces alongside other capabilities like real-time engraving previews, drag-and-drop functions, and tutorials. The best machines serve many project needs, and robust software support is a top contributor to achieving that.
How do you choose the best laser engraver for stone projects?
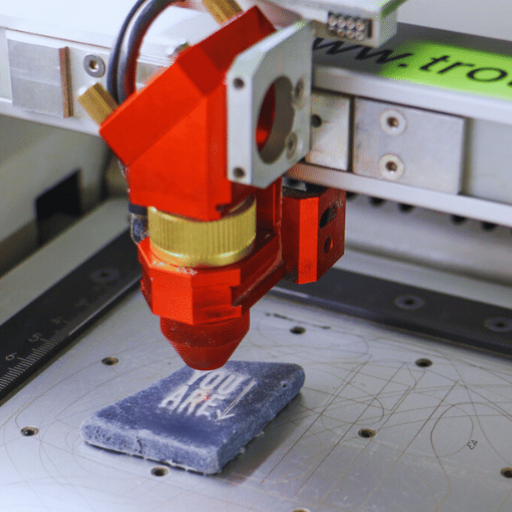
The best laser engraver for stone projects needs consideration of essential aspects such as the laser power, material type, and precision. For instance, a 40W or higher laser engraver is ideal for efficiently engraving hard materials like stone. Some stone types may not fully respond to laser processes, so ensure the machine you choose is compatible with your selected stone type. High-resolution precision is achieved in finer-detail engravers, so check the engraving output before purchasing. Moreover, the scope of user support and compatibility with reliable software can significantly help project execution.
Comparing CO2, fiber, and diode laser engravers for stone
As for engraving stone, CO2, fiber, and diode laser engravers, each has its strengths and weaknesses. CO2 lasers are popular for engraving because they are versatile and can work on many non-metal materials, including stone. However, higher watts might be necessary for more challenging rocks like granite. Fiber lasers, in contrast, are best known for marking metals and tend not to be recommended for stone projects because they are incompatible with the material. While diodes are cheaper and more convenient due to their small size, they generally do not have enough power to engrave dense stones. Therefore, CO2 laser engravers with high wattage are most effective when stone engraving is the objective.
Assessing your project needs: From small tiles to large slabs
The size and type of stone materials determine the appropriate type of laser engraver. If the project consists of decorative tiles or intricate patterns, a mid-range CO2 laser engraver shipped with matching bed size is a satisfactory option. Slabs will need a powerful laser and an engraver capable of handling substantial weight and size for architectural or memorial works. These specific tasks are enhanced further by using machines with adjustable worktables or pass-through capabilities. As the operator experience increases, the choice of laser engraver becomes more nuanced, especially in the case of intricate and complex designs that may require high precision and advanced software compatibility. Understanding specific restrictions for the engravers and aligning them with project needs will maximize efficiency while superposing the intended results and requirements.
Budget considerations: Entry-level vs. professional-grade machines
In the quest for entry-level and pro-grade laser engravers, I suggest contemplating the scale and frequency of your projects. Engravers at the entry-level offer great value for money and are best suited to hobbyists or small-scale operations. These machines usually have lower power and fewer features but handle simple tasks reasonably well. On the other hand, professional-grade engravers offer the most features, have the most incredible power, and are the most durable. Although these are the most expensive, they are essential for heavy-duty projects or commercial purposes. The investment for professional grade models is substantial, but businesses will benefit from the value they create over time and their faster processing speeds. Ultimately, it is a matter of how well you can balance your budget, your application needs, and production targets.
What are the steps to successfully engrave stone using a laser machine?

Preparing your stone surface for laser engraving
My first step in prepping your stone for laser engraving entails cleaning the stone of any dirt, dust, or oil residues that could hinder the engraving process. This can be accomplished by using a damp cloth or soap and water. However, I ensure the stone is completely dry before starting my next step. I then check the flatness of the stone’s surface since flatter surfaces guarantee improved results during engraving. If necessary, I lightly sand the stone to achieve the desired texture. Finally, I clamp the stone onto the laser engraver so that the tool does not move during the engraving process. Shakiness can severely compromise the quality of the work. Having the stone prepared beforehand plays a massive role in engraving quality.
Setting up your laser engraver and adjusting laser settings
Before turning the machine on, check that it is placed on a flat and steady table, as this is the first step in setting up your engraver. Next, check that all the wires, including power and data cables, are plugged in correctly. Once the machine is on, ensure the engraver is calibrated according to the instructions. The engraver’s calibration significantly impacts its precision and correct alignment.
Now, pick the correct values for laser power and speed according to the type and density of the stone material. Softer stones require less power so that they are not overburned. Aim the laser at harder stones like granite and marble with higher power and lower engraving speeds so more defined marks are created. Testing a minor area or a spare piece of the same material is advisable to fine-tune these parameters. Make sure that the energy delivery is optimal by adjusting the focus of the laser head so that the correct focal distance is set between the stone and the laser. Focus the laser on the stone surface.
Finally, recall any necessary parameters in the design editor, like resolution and engraving depth, and upload the design files to the engraver. Before commencing work, look at all settings to detect any possible issues. To reduce errors, set up the parameters and make precise adjustments to the laser. This permits detailed and professional laser engraving results.
Tips for achieving intricate designs and deep etching on stone
In steining stone, my attention is primarily set on their exceptional designs and etching depth. This starts with an upload of the work to the design software and setting the design resolution to 600 DPI. This ensures that all details are as straightforward as possible. I changed the settings covered here in small increments regarding the laser power. Rather than accomplishing that surreal single pass of high power, I prefer to use moderate multiple passes to reduce the probability of cracking or discoloration. Moreover, I check the cleanliness and flatness of the stone surface since any dust or unevenness on it will diffuse the laser energy and lose precision. I can also use masking tape on scorched lighter stones to avoid the burn from sawing. This would improve the design aspect of the stone.
What are some creative applications for laser engraved stone products?
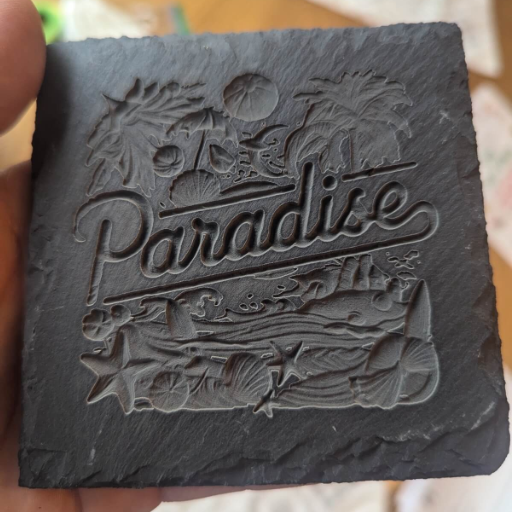

Embellishing a stone through engravings can be versatile, having functional and decorative characteristics. It can be used as art or sculpture, making it perfect for home decor, memorial plaques, engraved headstones, and various coasters and tiles. Moreover, its durability makes stone often used as keepsakes or treasured items. In the corporate world, businesses often use engraved stones as promotional gifts or custom signs due to the professional, unmatched finish they offer. Custom jewelry also benefits from stone engraving as some intricate designs may carry sentimental value, serving as absolute art pieces. The aesthetic appeal and the functional ability of engraved stones make it a very versatile piece of art.
Personalized gifts: Engraved marble coasters and granite plaques
Marble coasters and granite plaques as personalized gifts are on-demand because of their never-ending beauty and strength. Granite plaques and engraved marble coasters are popular for personal gifts because of their beauty and durability. Marble coasters are ideal for weddings, anniversaries, or housewarming events because they can be engraved with meaningful quotes, intricate patterns, or monograms. Their polished surfaces protect furniture from damage and bring in elegance. On the other hand, granite plaques are often used to display family names, inspirational messages, or artwork. They serve as decorative items or commemoration pieces. Laser engraving ensures that marble and granite are sharper for longer and that treasured keepsakes last for any special occasion.
Architectural elements: Laser-etched tiles and stone signage
Laser-etched tiles and stone signage are the most efficient tools for marrying precision with durability, making these ideal for architectural functions. This technique enables crisp cuts that withstand environmental conditions, from detailed engravings on floor tiles to the detailed lettering needed for wayfinding or building identification. Tiles can be modified to feature logos, mosaics, or exquisite textures, beautifying spaces. So, with signs—in stone, precise etching ensures permanent clarity so it can be placed within and outside public buildings, residential blocks, and corporate offices.
Memorials and commemorative pieces: Laser-engraved headstones and monuments
Using laser engravers to prepare headstones and monuments has dramatically improved the accuracy and detail of such artworks. Specially focused laser beams can etch letters, designs, and pictures to stone, such as granite or marble. These tributes are custom-made and can withstand harsh weather conditions, thus preserving them for a long time. Such headstones can also feature additional elements, including portraits, special symbols, or personal notes that ensure the memorial is remembered for years. Unlike traditional carving, laser engraving achieves higher precision and greater detail, all while skirting any risk to the materials being used. It has become the method of choice among families and institutions who seek tasteful commemorative items that will stand the test of time.
How do you maintain and troubleshoot your stone laser engraving machine?

Regular maintenance tips for optimal performance
Maintenance is crucial for a stone laser engraving machine’s performance and durability. Start by cleaning the machine after every use to stop dust, debris, and residue from accumulating on the glass lenses, mirrors, and rails, as this can reduce the effectiveness and precision of the machine. Always clean these sensitive parts using microfiber cloths and other non-abrasive cleaning materials.
Check how the laser systems are aligned regularly, as this will ensure the quality of the engravings on the stone is precise and detailed. Also, remember to periodically check and tighten mechanical elements like belts and screws to maintain structural accuracy. Use manufacturer-approved lubricant on moving parts like guide rails and linear bearings to ensure they function correctly.
Continuously monitor the coolant levels or airflow in the air-cooled system to ensure it remains in peak condition. Regularly clean cooling vents and filters to prevent overheating, which can damage the laser source. Finally, occasionally adjust the laser power settings so that the laser engraver does not excessively wear out, and you can get accurate engravings.
Finally, as with any equipment, update the firmware and software tools recommended by the manufacturer to match the latest functionalities and safety protocols. Proper and consistent maintenance prolongs the equipment’s life and ensures high-quality engravings each time it is used.
Common issues and their solutions when engraving stone
An engraving stone concern that many have is the depth of the engraving not being uniform across the stone. This primarily occurs due to improper laser power settings or the stone’s rough surface and different levels. I resolve this by vigorously cleaning and leveling the stone before engraving and setting the laser power level to an appropriate level for the material’s strength. A handful of test runs often helps with fine-tuning the setup.
Chipping or cracking during the engraving process is another common problem. This occurs when the intensity of the laser beam is set too high, or the material being engraved is too fragile. To mitigate this, I lower the speed and power used for the laser but keep the power set high enough to retain the stone’s strength. Ensure that the stone is adequately secured to avoid unnecessary movement. Using masking tape on delicate stones can also reduce cracks.
Achieving insufficient contrast is usually very complicated, especially with pale colored stones. I go a step further by darkening the stone using solutions or paint after the process; this enhances the contrast and ensures the engraving is good-looking.
When to seek professional help for your laser engraver
While adjusting settings or recalibrating does not solve persistent issues, consulting a professional for valuable insight is best. If you find the controls unresponsive or the machine continuously overheating, it could be a power output issue affecting the overall system stability. Such problems need diagnosing with the appropriate tools for both the software and hardware parts because they’re often misaligned and cause malfunctions. Moreover, signs of critical damage to components or materials due to overexposure to lasers would indicate a misalignment in the module system. From my experience, these professionals help with upgrading the system beyond my ordinary scope of maintenance, installing parts like more powerful lasers, or replacing vital components. Specialized knowledge allows these experts to manage systems continuously, enabling the machine to work reliably and safely for users.
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What types of laser engraving machines are best for stone engraving?
A: CO2 laser engravers and fiber laser machines are the most effective options for stone engraving. CO2 laser engravers are versatile and work well on various types of stone, while fiber lasers are particularly suitable for more complex materials like black granite or quartz. The choice depends on the specific stone you’re working with and the desired engraving results.
Q: Can a CO2 laser engraver effectively cut and engrave stone?
A: A CO2 laser engraver can effectively engrave stone, but its cutting capabilities are limited. A 130W CO2 laser or higher for engraving is recommended for precise, detailed results on most stone surfaces. However, you may need to consider more powerful laser-cutting machines or specialized stone-cutting equipment for cutting stones.
Q: What is the difference between fiber and CO2 laser for stone engraving?
A: Fiber and CO2 lasers differ in their wavelengths and how they interact with materials. Fiber lasers are more effective on metals and harder stones, producing crisp, high-contrast engravings. CO2 lasers work well on a broader range of materials, including softer stones, and can achieve deeper engravings. The choice depends on your engraving project’s specific stone type and desired outcome.
Q: What types of stone can be engraved using a laser engraving machine?
A: Laser engraving machines can work with various types of stone, including marble, granite, slate, sandstone, and quartz. Some stones, like black granite, are particularly well-suited for laser engraving due to their high contrast when engraved. The success of the engraving process depends on the stone’s composition and the power of the laser used.
Q: How does a stone engraving machine compare to a CNC machine for engraving rocks?
A: A stone engraving machine using laser technology offers precision and speed, making it ideal for intricate designs and logos on various stone surfaces. CNC machines, on the other hand, use physical cutting tools and can achieve deeper engravings and 3D effects. Laser engraving is generally faster and requires less maintenance, while CNC machines offer more versatility in depth and texture.
Q: What safety precautions should be taken when using a laser stone engraving machine?
A: Always wear appropriate safety glasses to protect your eyes from the laser beam when using a laser stone engraving machine. Ensure proper ventilation to remove any dust or fumes generated during engraving. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for machine operation and maintenance. Keeping the work area clean and free from flammable materials is also essential, as some stones can heat up significantly during engraving.
Q: Can laser cutting machines be used to engrave and cut stone?
A: While laser cutting machines are primarily designed for cutting materials, many can also perform engraving tasks. However, when it comes to stone, most laser cutters are limited in their ability to cut through thick or dense stone materials. They are more commonly used for engraving and surface marking on stone. For substantial stone cutting, specialized stone-cutting equipment is usually required.
Q: What is the ultimate guide to achieving precise engraving results on stone surfaces?
A: The ultimate guide to clear stone engraving includes selecting the right laser type and power for your specific stone, properly focusing the laser beam, adjusting speed and power settings for optimal results, and preparing the stone surface. Testing your settings on a sample piece before engraving your final project is crucial. Experiment with multiple passes for deeper engravings, and consider using engraving tools or aids to enhance the engraved area if needed.
Q: Is laser engraving on uneven or curved stone surfaces possible?
A: Laser engraving on uneven or curved stone surfaces is possible, but it requires careful setup and potentially specialized equipment. Some advanced laser engraving machines have auto-focus features or rotary attachments that can adapt to irregular surfaces. For best results, it’s essential to ensure that the laser beam remains focused on the stone’s surface throughout the engraving process, which may require manual adjustments or custom fixtures.
Q: What are the advantages of using laser engraving over traditional engraving methods for stone?
A: Laser engraving offers several advantages over traditional stone engraving methods. It provides precise and consistent results, allows for intricate designs and small text, and is generally faster than manual engraving. Laser engraving is also non-contact, reducing the risk of damaging delicate stones. Additionally, it offers greater flexibility regarding design changes and can quickly reproduce complex patterns or logos. However, traditional methods may still be preferred to achieve certain textures or deep engravings.









