In the global food industry, pasta stands out as a staple that transcends cultural boundaries, thanks to its versatility and simple yet delightful taste. This blog post explores the fascinating world of the largest pasta producers, focusing on their innovative production techniques and substantial impact on international markets. We will dive into the methodologies that distinguish these giants in pasta production, examine the global demand that drives their expansive operations, and consider the sustainability practices they adopt to maintain their competitive edge. By unraveling the intricacies of pasta production and international trade, this article aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of how these producers satisfy our love for pasta while shaping culinary trends worldwide.
Who is the Leading Pasta Producer in 2023?
In 2023, Barilla retains its position as the world’s leading pasta producer. Established in Parma, Italy, Barilla has become a global powerhouse in the pasta industry, renowned for its quality and extensive product range. The company leverages advanced manufacturing techniques and continuously innovates to meet diverse consumer tastes. With a commitment to sustainability and environmentally friendly practices, Barilla not only satisfies global demand but also sets industry standards in responsible production.
Understanding the Global Pasta Market
The global pasta market thrives on diversity and adaptability. In 2023, its growth owes much to expanding consumer preferences and innovative culinary applications. Italy, the US, and Brazil lead in both consumption and production. E-commerce and health-conscious products like gluten-free and whole grain pasta further fuel market expansion. Major players invest in sustainable sourcing, ensuring environmentally friendly practices. As new trends emerge, producers prioritize efficiency and quality, aligning with global demand while setting future culinary directions.
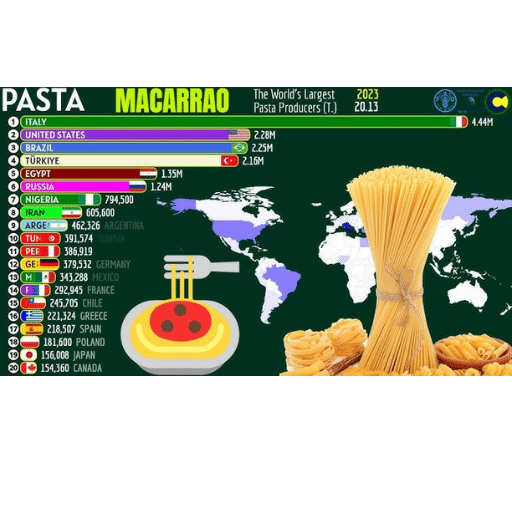
Key Countries in 2023 for Pasta Production
In 2023, I find that Italy, the United States, and Brazil dominate pasta production. Italy’s rich tradition and quality standards make it a leader. The U.S. pairs its innovation with high consumption rates, supporting its position. Brazil’s growing market caters to both regional and international demands, solidifying its role in global production. By focusing on efficiency and sustainable methods, these countries set the benchmarks in the industry.(Recommended: Spaghetti Production Line)
The Role of Durum Wheat in Pasta Production
Durum wheat plays a crucial role in pasta production due to its high protein and gluten content, which provide the necessary firmness and elasticity for pasta. This type of wheat ensures the pasta maintains its shape during cooking, resulting in the desired texture that resists mushiness. The high-quality semolina derived from durum wheat is a key ingredient that enhances the pasta’s ability to absorb flavors. Producers often choose durum wheat for its golden yellow hue, giving the pasta an appealing appearance. The unique qualities of durum wheat make it irreplaceable in producing high-quality pasta globally, contributing to the success of leading pasta-producing countries.
How Does Pasta Export Affect the Global Market?

Pasta exports significantly impact the global market by increasing international trade and fostering economic growth. Countries with strong pasta industries, like Italy and the U.S., benefit from exporting, as it boosts their economies through increased revenue. This trade also encourages culinary exchange, leading to greater cultural connectivity. As demand grows, pasta exporters must innovate and maintain high standards, influencing global production trends and setting benchmarks in quality and sustainability. Consequently, the pasta export market stimulates competition, promotes efficiency, and diversifies food offerings worldwide.
The Impact of Major Exporters on the Pasta Industry
Major exporters heavily influence the pasta industry’s landscape. Italy spearheads this impact by prioritizing quality and leveraging cultural heritage, which helps it dominate markets globally. The U.S. contributes by incorporating innovative production methods and expanding into emerging regions, fueling industry growth. Turkey’s role, characterized by competitive pricing and strategic market focus, further amplifies global pasta consumption. These exporters collectively enhance the industry’s dynamism, promoting diversity in pasta offerings and setting high benchmarks for quality and sustainability. Consequently, these major players not only shape consumer preferences but also steer global production trends.
Trends in Pasta Export for 2024
In 2024, pasta exporters will focus heavily on sustainability and innovation. Expect to see more pasta made from alternative grains and plant-based ingredients, catering to health-conscious consumers and diverse diets. Digital transformation will streamline supply chains, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Key markets will expand in Asia and Africa, with rising incomes and changing diets driving demand. Exporters will also prioritize eco-friendly packaging, reducing environmental impact and meeting consumer expectations for sustainable practices. As these trends take hold, the pasta industry will continue to grow, adapt, and meet shifting global preferences.
What are the Leading Countries in Pasta Production?

Italy remains the leader in pasta production, known for its high-quality durum wheat pasta and extensive variety that reflect its rich culinary heritage. Following Italy, the United States plays a pivotal role with its advanced manufacturing technologies and capacity to cater to diverse consumer preferences. Brazil is also a significant player, leveraging its abundant wheat resources and growing domestic market. Additionally, Russia’s production has been expanding, supported by increasing domestic demand and investments in production capabilities. Each of these countries not only contributes substantial quantities to the global market but also underscores the importance of embracing efficiency and innovation in production methods.
Top Exporters and their Contribution to the Market
Italy leads the global pasta export market, known for its tradition and quality, which drive strong international demand. Italian pasta brands dominate supermarket shelves worldwide, showcasing a rich variety of options. The United States follows, using advanced production techniques to cater to a wide range of tastes and dietary needs. Its exports capitalize on innovation and adaptability, enhancing its market reach. Turkey ranks third, benefiting from strategic geographic positioning and cost-effective production processes, allowing it to competitively supply Europe and neighboring regions. These countries anchor the global pasta market, making significant contributions through both volume and diversity.
Comparison of Fresh Pasta and Dry Pasta Production
There are some key contrast differences between the production of dry and fresh pasta, such as the components and processes, and even the shelf of the finished product. The common ingredients for fresh pasta generally contain eggs and all-purpose flour which results in a moister dough and a softer finish and is mostly done in smaller quantities. This type is more ’perishable’ and has a limited shelf life, usually needs to be eaten within a few days. Whereas, dry pasta production method involves the use of durum wheat semolina and water, which enables the manufacturing of pasta that can be kept at room temperatures for six months. In fact, dry pasta is produced in large quantities most likely using the extrusion & drying method which makes it easy to sell or export on a large scale.
What is the History of Pasta?

The history of pasta dates back to ancient times, with its origins believed to be from the Sicilian island, influenced by Arabic culinary traditions. Historical accounts suggest that pasta was first introduced to Italy by the Arabs during their conquest of Sicily in the 9th century. However, ancient wheat and noodle references can also be traced back to China and the eastern Mediterranean. Pasta became a staple in Italian cuisine during the Middle Ages, with dried pasta gaining popularity for its long shelf life, making it a convenient and versatile food source. By the 13th century, pasta production spread throughout Italy, further propelled by the invention of pasta-making devices during the Renaissance. The 19th and 20th centuries saw pasta’s global expansion, particularly with Italian migration, embedding it as a key culinary component worldwide.
The Evolution of Pasta Production
Pasta production has evolved significantly over the centuries, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands. Initially, people made pasta by hand, combining simple ingredients like wheat and water. During the Renaissance, innovation led to the development of basic pasta-making devices, which allowed for more consistent shapes and textures. The Industrial Revolution further transformed production with the introduction of mechanized equipment, enabling mass production and distribution. In the 20th century, the manufacturing process advanced with the use of extrusion machines, precision drying methods, and quality control standards. Today, pasta makers focus on efficiency and sustainability, incorporating high-tech machinery and sustainable practices to meet global demands while ensuring product quality and minimizing environmental impact. These advancements have made pasta an accessible staple throughout the world.
Influence of Italian Pasta on Global Cuisine
Without a question, Italian pasta has brought a great deal of flavor and extremely rich traditions to various cultures around the world. Today, pasta is becoming a part of many countries’ cuisines, which is being modified to fit the people of that nation. Pasta was then brought to America through Italian immigrants where it was incorporated into dishes like spaghetti and meatballs. In Asia, there are also Italian pasta and techniques used, for example, in pasta with soy sauce or seafood, which combines Italian and Asian culinary traditions. Because pasta is so versatile, it goes well with almost any kind of sauce, meat, or vegetable. Such considerable spread further substantiates and emphasizes the fact that pasta is one of the true universal cuisines which can easily be found in almost every culture enhancing the already existing culinary fabric of the culture.
Significant Milestones in the Pasta Industry
The pasta industry has undergone several key milestones that shaped its global presence. In the early 1800s, Naples became a hub for dried pasta production, benefiting from sunny weather that facilitated natural drying. The introduction of industrial roller technology in the 19th century revolutionized the process, making pasta production faster and more consistent. By the mid-20th century, advancements in packaging technology extended pasta’s shelf life, enabling global distribution. The 1970s saw a surge in pasta’s popularity due to increased marketing efforts and the carb-loading trend among athletes. More recently, innovations like creating whole grain and gluten-free options have catered to health-conscious consumers, positioning pasta as a versatile and enduring staple in modern diets.
What are the Trends in Pasta Consumption?

In recent years, pasta consumption trends have evolved to reflect changing dietary preferences and lifestyle choices. A significant trend is the growing demand for healthier pasta options, such as whole grain, high-protein, and gluten-free varieties, catering to health-conscious and dietary-restricted consumers. Plant-based pasta alternatives made from legumes or vegetables are also gaining popularity, aligning with the increase in vegetarian and vegan diets. Additionally, there is a shift towards artisanal and organic pasta, with consumers seeking premium products that emphasize quality and sustainability. The convenience of ready-to-eat and quick-cook pasta products is also driving growth in the market, appealing to busy lifestyles that prioritize time-saving meal options. Overall, these trends demonstrate the pasta industry’s adaptability to meet diverse consumer needs while maintaining its global appeal.
Global Per Capita Consumption of Pasta
The global per capita consumption of pasta varies significantly across different regions, with Europe and the Americas leading. Italy remains the top consumer, with an average of more than 23 kilograms per person annually, cementing its status as the home of pasta. Other European countries like Germany and France also exhibit high consumption rates. In the Americas, the United States and Brazil show considerable pasta consumption due to the diverse food culture and popularity of Italian cuisine. In contrast, Asian and African countries have lower per capita consumption, though interest is growing due to globalization and increased availability of pasta products. This increasing demand in various regions highlights pasta’s significant role in global diets, catering to local tastes and health considerations.
Factors Influencing Pasta Consumption Patterns
While exploring factors influencing pasta consumption patterns, I found several key aspects. Firstly, cultural heritage plays a profound role, especially in countries like Italy, where pasta is a staple. Secondly, economic factors, including affordability and accessibility, significantly affect consumption. Lower prices and more availability often lead to higher consumption rates. Thirdly, health trends increasingly impact pasta consumption. Many people now prefer healthier alternatives, such as whole grain or gluten-free pasta, aligning with modern dietary preferences. Lastly, marketing and branding strategies influence consumer choices, as brands that underscore quality or authenticity often enjoy more popularity.
Emerging Markets for Pasta
Emerging markets for pasta are experiencing rapid growth due to globalization, urbanization, and increased disposable incomes. In Asia, India and China lead this growth by adopting Western eating habits and valuing convenience in meals. In Africa, nations like Nigeria and Kenya have seen a surge in pasta consumption, driven by a youthful population eager to diversify their diets. The Middle East, with its rising middle class, also shows potential, particularly in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia. Brands are tailoring their products to local preferences, offering flavors and pasta types that align with regional tastes and dietary needs. As more people embrace pasta as a versatile and easy-to-prepare dish, these emerging markets continue to offer significant opportunities for expansion.
References
-
Top 9 Pasta Companies in the World – IMARC Group – Lists leading pasta manufacturing companies globally, including Barilla, Nestle, and De Cecco.
-
Barilla (company) – Wikipedia – Provides detailed information about Barilla, the world’s largest pasta producer.
-
Global Pasta Strategic Business Analysis Report 2024-2030 – GlobeNewswire – Offers insights into the global pasta market size and growth projections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Who is currently the world’s largest producer of pasta?
A: Italy holds the title as the world’s largest producer of pasta, generating a significant portion of the global supply. The country is known for its rich history in pasta production and remains a leader with its numerous pasta factories.
Q: How much pasta did the world’s top producer export in 2022?
A: In 2022, Italy, the world’s top exporter of pasta, exported approximately 6.2 million tons of pasta, contributing significantly to global pasta trade.
Q: What percentage of total EU pasta production does Italy account for?
A: Italy accounts for a substantial percent of total EU production, often exceeding 60%, due to its extensive network of pasta factories and high domestic and international demand for pasta.
Q: Which countries are the largest importers of Italian pasta?
A: The largest importers of Italian pasta include the United States, Germany, and France, reflecting a high international demand for quality pasta products.
Q: How has pasta production changed from 2021 to 2022?
A: Pasta production saw a slight increase from 2021 to 2022, driven by rising global demand and Italy’s capacity to scale production within its established pasta factories.
Q: What are the most popular types of pasta exported from Italy?
A: The most popular types of pasta exported from Italy include uncooked pasta such as spaghetti, penne, and fusilli. These varieties are staples in international pasta dishes.
Q: How does Eurostat contribute to the understanding of pasta production and trade?
A: Eurostat provides comprehensive statistical data on pasta production and trade within the EU, helping to track trends, production volumes, and the economic impact of pasta in the world market.
Q: What role does Tunisia play in the global pasta market?
A: Tunisia is known as a significant exporter of pasta, with a growing reputation for producing quality pasta products that compete on the international stage.
Q: How is pasta typically stored and sold to maintain quality?
A: Pasta is sold in airtight packaging to preserve freshness. To ensure longevity, it is best to store pasta in a cool, dry place, away from moisture and direct sunlight.
Q: What factors are driving the demand for pasta worldwide?
A: The demand for pasta is driven by its versatility in dishes, ease of cooking, and the growing popularity of Italian cuisine globally. Economic factors, such as affordability and the rise of pasta as a staple food in many countries, also contribute significantly.










