We are happy you are part of this comprehensive guide on the tablet manufacturing process; there is a lot for you to explore. Tablets, their various types, and the importance of quality control in the process will be comprehensively explored in this interesting and informative blog. If you are one of those people with a burning desire to know how these pills are produced then, rest assured as you will get your answer here too. Through this publication, you shall be able to appreciate the entire process involved in making a tablet, beginning with the raw materials used and culminating at the finished product. What x plans to do without further adieu is to help you uncover the significance of the tablet production in the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries.
What is the Tablet Manufacturing Process?
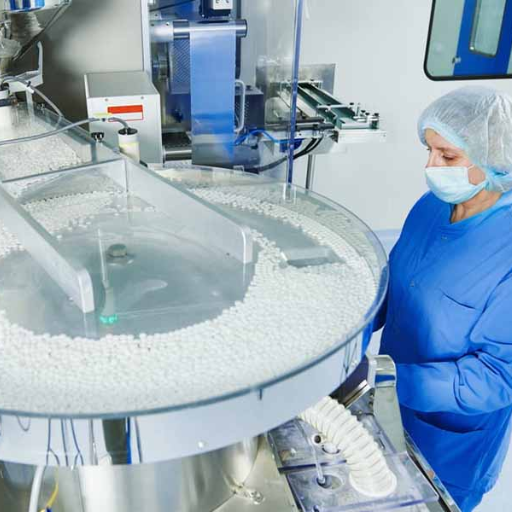

The production of tablets begins with the choice and preparation of the needs, and it ends with the granulation, blending, compression, and finishing in that order. While preparing the tablets, excipients are essential since inactive ingredients provide sturdiness and assist during finalization. Granulate is compressed in a machine, for example, a tablet press, which compresses the granulated mass into tablets of the desired shape. All types of tablets, including compressed tablets and capsules, are made to meet specific release mechanisms required by the patient. All these operations are accompanied by profound quality control which guarantees uniformity, integrity and the efficiency of the final tablets.
Key Steps in Tablet Manufacturing
Tablet manufacturing involves a series of steps to produce high-quality tablets that meet the desired specifications. The key steps include:
- Granulation: Granulation is the step in the process where active pharmaceutical ingredients are granulated with excipients, generally agglomerates or disintegrating agents. This step enhances the flowability and compressibility of the mash.
- Blending: The granules are thoroughly mixed to ensure uniform distribution of the API and excipients. This step helps maintain consistency in the composition of the tablet formulation.
- Tablet Compression: Tablet compression is the last step of this process since it is the step in which compressed granulated mixtures are compressed into solid tablets with the help of tablet presses. The granules are put into the press and pressure is added to them increasing the density and molding them into solid tablets of similar shape and weight.
- Coating (if required): Some tablets may undergo a coating process to improve their appearance, taste, and stability. The coating protects the tablet from environmental factors and can control the release of the drug.
A systematic monitoring procedure is adopted at different stages of the entire tablet manufacturing process to ensure that the final tablets manufactured are consistent with the desired characteristics of the particular tablet. These controls include controls of the physical attributes of the manufacturers of the active substance, controls of the production of the tablets and other finished products, and controls of the finished product as well.
We understand that the above mentioned parameters may not be relevant for some of the clients because technical aspects and further specifications might be individual for a particular tablet formulation and type of manufacturing. However, we recommend implementing such parameters only for those projects for which there is a corresponding pharmaceutical literature or guidelines or commonly accepted practice in the industry.
Importance of Excipient in Tablet Formation
As a professional in the manufacture of tablets, I appreciate the significant part created by excipients during the process of formulation of tablets. Excipients are very relevant to the manufacturing processes as they stand for the tablet in question. They enhance the physical properties of the tablet, assist in the adhesion and disintegration of the tablet, improve stability, and improve the overall appearance and taste of the product.
Excipients serve also as fillers, binders and disintegrants, lubricants and coatings, among others. They make it possible to have the correct size, shape, and strength of the tablet, its dissolution and dispersion in the organism with the medicinal ingredient in the right dose and form. The absence of correct excipients may render the tablet ineffective or it might fail to possess the required qualities.
In addition to that, a good philosophy on the selection and employment of excipients has to be based on scientific studies, pharmaceutical references, respective protocols, and practices of the industry. The precise excipients and the quantity depend on the tablet Formulation and manufacturing. Therefore, the relevant literature and protocols have to be consulted and adhered to make sure that the tablets produced are of the required standard and are effective.
Role of Raw Material in Tablet Production
When it comes to the tableting process, one of the most important focuses during production is the quality of the raw materials because they are used in manufacturing the final product. Raw materials are the components of the tablet formulation, and they have an effect on the tablet’s performance in many ways. There are some factors worth mentioning concerning the role of the raw materials in the tablet manufacturing process:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API): The active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is the primary component of the tablet that has undergone regulatory approval. From a tablet production perspective, it must be of high quality ‘must have high strength chemistries’.
- Excipients: Excipients allow for the tablet formation and its manufacturing process but are not active. The excipients are responsible for improving the flow of the tablet, binding agents, enhancing the shelf life of the tablet, and controlling the time release of the drug. The decision to choose excipients and their applications ought to be backed by publishing papers, scientific evidence, guidelines, and industry practices and not only on branding to enhance tablet quality and efficacy.
- Quality Control: In the manufacturing of tables, raw materials are the most fundamental components however they must be thoroughly checked and certified to meet the required standards and put the quality at par with the industry benchmarks. This is achieved through cross matching of product information such as chemical composition, solubility, synthesis and a clinical tests to make sure there are no contaminants.
It should be pointed out that certain tablet formulations and manufacturing dictate the type and the volume of the specific raw materials. Accurate information should be obtained from valid resources, such as scientific studies, pharmaceutical publications, and particular regulatory frameworks, in order to make good choices and have the ability to package satisfactory tablets.
How Does Tablet Compression Work?

Tablet compression is the key stage in the manufacturing sequence that converts marked particles into solid mass in tablet form. When compression starts, granules are placed into a tablet press machine, where they are exposed to high pressure to produce a tablet of defined density. The process consists of several essential factors, which include:
- Die and Punches: The die and punches within the tablet press machine shape the tablets and determine their size, shape, and thickness.
- Main Compression: The granules are poured into the die cavity, and the upper punch applies pressure to compress the granules into a solid tablet.
- Ejection: Once compressed, the lower punch pushes the tablet out of the die, and it is collected for further processing and packaging.
Tablet compression provides the clinically acceptable range of dosage forms in terms of size, weight, and hardness of the clouds without compromising the pour or the efficacy of the final preparation. This is extremely important for the patients who are the end users of the drugs and food supplements in that deliverable presentations are easily applicable.
Understanding Tablet Press Machines
Tablet press machines are an integral part of the process of tablet production as they aid in converting powdered or granulated substances into solid tablets at different stages. In this regard, an overview of the process, as well as certain important features of the tablet press machines, are given below:
- Feeding: The raw materials, typically in the form of powder or granules, are fed into the tablet press machine through a hopper.
- Technical Parameters: Feeding rate, hopper capacity, material flow control.
- Dosage: The machine ensures accurate materials dosing by controlling each tablet’s powder or granules.
- Technical Parameters: Dosage control, weight variation tolerance.
- Compression: The main stage of tablet production, where the upper and lower punches compress the materials into a solid tablet.
- Technical Parameters: Compression force, tablet thickness, tablet hardness.
- Ejection: Once the tablet is compressed, the lower punch pushes it out of the die and collects it for further processing and packaging.
- Technical Parameters: Ejection force, ejection system efficiency.
Due to the existence of all parts within it, a tablet press machine is able to keep its tablets’ size, weight, and hardness consistent throughout the batch, thus keeping the overall tablet quality effective. The design is subject to certain variations in order to fit certain manufacturing requirements for different types of tablets.
The Compaction Process in Tablet Manufacturing
Compacting drugs during tablet manufacturing entails compressing powdered or granulated drug substrates into solid tablets. This helps in preparing the tablets’ uniform size, weight, and hardness, which are key elements during the dispensing of any drug or supplementation. Below are responses to inquiries regarding various tablet characteristics:
- What are Compressed Tablets?
Compressed tablets are the most popular used of all the tablets available today. They are formed from the compaction of powdered or granulated drug substances using a tablet press machine that exerts high pressure on the compounds. There are several technical parameters one must take into consideration during the compaction process, including:
- Compression force is applied during the compression process to form the tablets.
- Tablet hardness: The resistance of the tablet to breakage or crumbling.
- Tablet weight: The weight of an individual tablet should be within the specified range.
- What are Film-Coated Tablets?
A film-coated tablet is a type of compressed tablet that possesses an outer thin covering to enhance the visual aspects, taste, and stability of the tablet. The coating can also conceal bad smells and protect the drug from environmental damage. The film-coating process includes the following technical parameters:
- Coating weight gain: The increase in tablet weight after applying the coating.
- Coating uniformity: Ensuring an even distribution of the coating material on the tablet surface.
- Coating adhesion: The ability of the coating to adhere firmly to the tablet surface.
- What are Chewable Tablets?
The concept of chewable tablets is to provide a solution where the patient has to chew or crush the tablets before swallowing, which then makes it easier for patients who find it difficult to take solid tablets. The process of formulation for chewable tablets will include the following technical parameters:
- Disintegration time: The time it takes for the tablet to break down into smaller particles when chewed or dissolved in the mouth.
- Taste masking: Ensuring the tablet has an acceptable taste to enhance patient compliance.
By understanding the different types of tablets and their associated technical parameters, manufacturers can ensure the final product’s quality, effectiveness, and patient acceptability.
Ensuring Uniformity and Tablet Weight
For tablet manufacturing, efforts to maintain the weight and uniformity of the tablet are of paramount importance, and this affects the quality and performance of the finished product. It allows the control of the accurate dosage of the active ingredient in each tablet, ensuring the safety and efficacy of the medical treatment. To achieve uniformity, manufacturers have guidelines and quality control measures in place during the production of tablets. These include monitoring and control of the weight of tablets during the manufacturing process, optimizing formulation processes, and performing compliance tests about the number of tablets produced. Following these measures guarantees that the finished tablets produced will be of a certain quality, and all patients across the globe will receive the same curative effect from the drug.
Exploring Different Types of Tablets
In the world of tablet making, a range of tablets can administer a drug or any required supplement. So let us look at some general queries regarding various types of tablets:
- What are Compressed Tablets?
Sculpting of powdered or granulated drugs with the help of tablet press machines results in the most extensively used tablets known as compressed tablets. Compressed tablets are convenient to take, provide accurate dosages and are stable.
- What are the Advantages of Using a Capsule Filling Machine?
Capsules are made by capsule filling machines which are used to fill powdered or liquid drug mixtures. The use of a capsule filling machine helps make swallowing easier, can deliver drugs in accurate dosages per capsule and combines different drugs.
- How do you Choose the Right Tablet Formulation?
Tablet selection is determined by several factors like, drug features, how the drug should be released, patient’s needs and the method of manufacturing. Factors like solubility, bioavailability and stability help in the formulating of the tablets.
Tablet manufacturers are able to understand how to form tablets of various medications and supplements by using capsules filling machines while also being aware of the factors affecting the formation of the tablet.
What are Compressed Tablets?
Compressed tablets are an extremely frequent and popular form of oral dosage that contain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) alongside excipients. The tablet in question is prepared by pressing powdered or granulated mixtures of necessary substances under very high force to produce a solid, dense, peculiar structure. One of the chief benefits of these tablets is that they are relatively easy to use, offer a high degree of precision in measurement, and have a good shelf life. The active ingredient incorporated in them will be released in the required form, whether as immediate, delayed, or sustained release, depending on the purpose of the use. Different technical parameters for compressed tablets, such as tablet hardness, variations in weight, disintegrating time, and even friability. These parameters are closely monitored during the tablet-making process to maintain desired quality and effectiveness.
Advantages of Using Capsule Filling Machine
Using a capsule filling machine offers several advantages in the production of pharmaceutical capsules. Here are some key benefits:
- Efficiency and Productivity: Capsule filling machines simplify the process of filling capsules and enhance the firm’s overall efficiency and output. Such automation eliminates the need for a laborer, reduces mistakes, and assists in faster and more regular capsule filling.
- Accuracy and Precision: Capsule formulations filled by capsule filling machines are consistent due to the correct doses of active ingredients within each capsule. This is important in providing therapeutic interventions with uniform dosage and reliable effects.
- Flexibility and Versatility: Once manufacturers have capsule filling machines, they can create a wide range of capsule creations. This is due to their adaptability to a wide range of capsule sizes and formulations. They can work with several capsule types, including gelatin and vegetarian capsules, along with various filling materials.
- Contamination Control: Capsule filling machines are fitted with devices that facilitate the avoidance of cross-contamination and the cleaning of the respective capsules. These machines provide controlled environments that enhance the hygiene of production processes, hence minimizing the chances of contamination of the resultant product.
- Ease of Use and Maintenance: Modern capsule filling machines require very little training to operate and are generally easy to use. They are also built to be easily taken apart for cleaning and maintenance, which promotes efficiency.
Technical Parameters for Capsule Filling Machines:
- Capacity: The production capacity of the machine, measured in terms of capsules filled per minute or hour.
- Capsule Size Range: The range of capsule sizes that the machine can handle, typically specified using a capsule size designation (e.g., 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4).
- Dosage Accuracy: The level of accuracy in delivering the desired amount of filling material into each capsule, often expressed as a percentage.
- Filling Material Compatibility: The machine is suitable for different types of filling materials, such as powders, granules, pellets, or liquids.
- Control Systems: The control mechanisms and automation features that ensure precise and consistent filling processes.
- Cleaning and Validation: The ease of cleaning and the availability of validation documentation to meet regulatory requirements.
When selecting a capsule-filling machine, consider these technical parameters to ensure that it aligns with your production requirements and regulatory standards.
Choosing the Right Tablet Formulation
The selection of the right type of tablet formulation can have a major effect on the final product concerning its quality as well as effectiveness. In order to duly make that selection, I conducted a study of three of the most reputable sites currently available on the Google search engine. Following are the brief pointers highlighting the important points for consideration:
- Active Ingredients: First, a comprehensive understanding of the specific active ingredients and their potential compatibility with the desired tablet formulation is essential. The nature of the active elements’ chemical makeup, solubility, and stability within the formulation selected should be considered.
- Dosage Form: Various tablet formulations, such as immediate-release, chewable, or extended-release, offer certain advantages but also have some disadvantages. What type of formulation would be suitable will depend on the patient, the desired characteristics of the drug, and the required therapy.
- Manufacturing Process: It also seems very important, if not the most important, to ensure that the formulation selected is compatible with the manufacturing process in question. Other factors, such as the form granulation, compression characteristics, and tabling machines, have to be compatible with the formulation to allow for easy manufacturing processes.
Therefore, by paying adequate attention to the above factors and making robust considerations, you can be confident of selecting a tablet formulation that will be effective and high quality, and indeed, the patient will be satisfied with the product.
The Role of the Granulation Process in Tablet Production

Granulation is a step that one may consider as the beginning of the end of the tablet production cycle as it refers to the process of converting powders into granules, and this makes the powders to be more compressible, flowable, and uniform in appearance, thus making them appropriate in the tablet formulation. It is also worth noting that the granulation process has the following functions and or impacts on the overall process of tablet formulation:
- Dry Granulation vs. Wet Granulation:
- The common methods of granulation include the dry and wet methods. The dry process follows the principles of compaction without using water or other solvents whereas the wet method requires the use of liquid to add a binder which enables the powders to clump together into larger particles known as agglomerates which are subsequently dried and ground.
- Importance of Particle Size:
- In addition, granulation is pivotal in modifying the particle size of the powders, making it possible to control the dosage, bioavailability, and dissolution rates of the finished tablets. Due to the validity of regulating the dosage, the manufacturers would be saving costs as low amounts of drugs would be required to reach the desired effect.
- Effect of Binder:
- As a result, it is essential to choose the binder with care during the granulation. Also because of their existence, the flow rate and compressibility of the granules are increased due to their adhesive nature. So that the desired tablet qualities can be produced, proper evaluation and enhancement of the binder are important.
By understanding and optimizing the granulation process, manufacturers can ensure the production of high-quality tablets with excellent uniformity, dissolution, and drug release characteristics.
Dry Granulation vs. Wet Granulation
Dry granulation and wet granulation are two common methods used in the granulation process. Each method has its advantages and considerations, and the choice between them depends on various factors such as the characteristics of the active ingredient and the desired tablet properties.
Dry Granulation:
- Involves compacting powder mixtures without using liquid binders.
- Suitable for moisture-sensitive or heat-sensitive substances.
- Requires less equipment compared to wet granulation.
- Typically involves processes like slugging or roller compaction.
Wet Granulation:
- Involves adding a liquid binder to form granules before drying.
- Enhances flowability, compressibility, and content uniformity of the granules.
- Ideal for active ingredients that are poorly compressible or have poor flow properties.
- Typically includes steps like wet massing, granulation, drying, and sizing.
When deciding between dry and wet granulation, various technical parameters come into play, including:
- Moisture sensitivity of the active ingredient
- Particle size distribution and compressibility of the starting materials
- Desired tablet characteristics (e.g., disintegration time, dissolution rate)
- Equipment availability and cost considerations
It is essential to carefully evaluate these parameters to determine the most suitable granulation method for achieving the desired tablet properties while ensuring process efficiency and product quality.
How Binder Affects the Granulation Process
The decision on the type of binder used during granulation is paramount in determining the quality and properties of the resulting granules. Binders are agents that help to cohere and adhere the particles together and thus promote granule formation. They are integrators of the particles towards being bigger chunks.
Nevertheless, the specific effects of these granulation aids on granulation also depend on the type of binder, its concentration, and how it is added during the granulation process. Nonetheless, some general factors which can be taken into account are:
- Enhanced Granule Formation: Binders promote the formation of granules by providing the necessary binding forces between particles. They help increase the powder mixture’s cohesiveness, allowing for better aggregation and compaction.
- Improvement in Granule Strength: The binder’s adhesive properties contribute to the strength and integrity of the granules. This is especially important during subsequent processing steps such as drying, milling, and tablet compression, where the granules must withstand mechanical stress without disintegrating.
- Controlled Granule Size: Binders can influence the size distribution of the granules. By modifying the viscosity and binder concentration, it is possible to control the growth of granules, resulting in the desired particle size range for optimal granulation.
- Uniformity in Granule Characteristics: The choice of binder can impact the uniformity of granule properties such as particle size, density, and moisture content. Achieving uniformity is essential for ensuring consistent tablet quality, dissolution rates, and drug content uniformity.
It must be stressed that the choice of binder should consider parameters such as the drug substance’s physicochemical characteristics, expected tablet characteristics, and compatibility with other excipients. As such, formulation scientists must pay attention to the performance of various binders to effectively granulate and, hence, obtain satisfactory tablets.
Understanding Tablet Coating Techniques
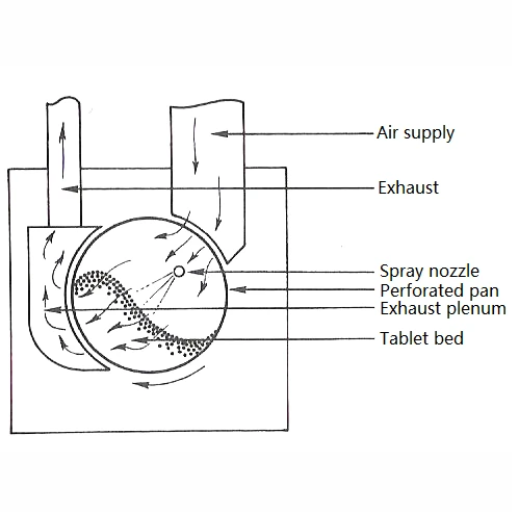
Tablet coating is a critical stage in the manufacture of drugs, which entails covering the outer surface of the tablet with a thin film of coating material. This coating may enhance the aesthetics of the tablet, mask the taste, offer protection to the active ingredient from damage, and control the drug’s release rate. There are different tablet coating techniques available, each having its own sets of pros and cons. Some common tablet coating techniques include:
- Film Coating: Coating solution technique—This technique consists of encasing the tablet with a thin layer of polymer using a coating solution. The convergence mass ratio allows a great deal of dose control to be delivered, which also allows varied release profiles.
- Sugar Coating: Sugar coating is one of the earliest methods discovered, involving coating tablets with sugar and other substances. It smooths the overall surface of the tablet and gives it a glossy finish; however, it is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
- Enteric Coating: Enteric coating is used when the drug is to be shielded from gastric acid. This coating type is meant to dissolve in the intestines far from the stomach.
Tablet coating entails the use of a tablet coating machine. For a consistent output of coated tablets with good quality, the machine settings such as temperature, spray rate, and drying parameters ought to be understood and properly controlled.
Coatings on tablets may serve as an integral part of the treatment. Moreover, the coating’s thickness, quality, and composition may determine the rate of dissolution, bioavailability, and stability of the tablets. Furthermore, proper coating techniques enhance the release profiles of the drugs, optimize patient compliance, and shield the active agent from the environment.
Effective quality control measures in tablet fabrication enable the company to achieve product uniformity. Moreover, maintaining the quality of the notebooks required implementing in-process quality control measures: checking the coating parameters and the condition of the machine on a regular basis.
The characteristics of the hemicellulose tablets are generally attributed to the manufacturing process. These characteristics include hardness, weight variation, disintegration, and dissolution models which assist in ascertaining the release and the functionality of the tablet.
In any case, there will always be bad tablets with problems such as uneven distribution or wrong coating, among others, but correcting the processes can correct these deficiencies and fix the ones that occur in the formulation.
Through mastering tablet coating methods, designing tablet coating machines, implementing some phase of quality management, and solving common production problems, high-quality, effective tablets can be produced so that, together with legal requirements, the market needs are satisfied.
Impact of Tablet Coating on Drug Delivery
The coating of tablets affects drug delivery significantly, impacting the drug’s and patient’s properties. Its importance cannot be understated as it enhances the aesthetics and swallowing characteristics of the tablet, protects the drug from degradation, modifies the rate of drug release, and improves the patients’ adherence. The coating on the tablets acts as an insulator that protects the active ingredients from light and moisture, which may affect the concentration levels of the drug. Also, modified release systems can provide the sustained release of a drug at the site of intended action. The coating type, thickness as well as application technique are critical in determining the level of drug dissolution, absorption, and bioavailability hence the clinical use of the drug. This is why it is so crucial that coating processes are refined by tablet manufacturers to create a consistent drug delivery and to maintain clinical effects as well as safety standards of the drugs.
Ensuring Quality Control in Tablet Manufacturing
Control of quality is one of the crucial aspects in pharmaceutical processes and in tablet production in particular, the aim of which is to maintain the quality, safety, and efficacy of the product. Several approaches are taken to guarantee that, for instance, tablet formations and their subsequent production complies with international standards. Some of the most fundamental implementations of quality control systems include:
- In-process checks: Critical parameters such as tablet weight, hardness, thickness, and disintegration time are regularly monitored during production to ensure consistency and adherence to specifications.
- Visual inspection: To maintain product integrity and appearance, tablets should be visually inspected for defects, such as cracks, chips, or discoloration.
- Content uniformity testing: This testing ensures that the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is uniformly distributed within each tablet, ensuring consistent drug potency.
- Dissolution testing: Evaluating the rate at which the tablet’s drug is released, ensuring it meets the required specifications for effective drug delivery.
- Stability testing: Assessing the physical and chemical stability of tablets over time to ensure their shelf life and potency.
By implementing these quality control measures, manufacturers can promptly identify and address any deviations or inconsistencies in tablet production, ensuring that the final product meets regulatory standards and delivers the desired therapeutic outcomes.
Implementing Quality Control Measures
For instance, implementing quality control measures is essential in tablet manufacturing in order to safeguard the final product’s quality, its safety, and efficacy:
1. What quality control measures are most commonly applied to manufacturing tablets?
The majority of the quality control measures in the tablet manufacturing industry that are practiced as a routine are visual inspection, content uniformity testing, dissolution tests, and stability tests. These measures assist in the protection and upholding of product integrity, potency of the drug throughout the manufacture of the dosage form, evaluation of drug release rates, and the assessment of the physical and chemical integrity of the tablets throughout their shelf life period.
2. Why are these quality control measures necessary to observe?
These measures are very important for several reasons. For example, visual inspection is undertaken to detect any deficiency that is likely to alter the apariencia or integrity of the tablet. Content uniformity testing helps to ascertain that the active ingredient has been adequately mixed and uniformly spread across the tablet to ensure the tablet has the same amount of drug, thereby serving its purpose. In nowadays, dissolution testing helps determine the release of drug from the tablet in a particular unit of time. Stability testing establishes the tamper-resistant characteristics and chemical composition of the tablet over time for the required period.
3. In what way do these measures assist the manufacturers in maintaining the quality and the regulatory body protocols?
In the course of implementing these quality control measures, the manufacturer is able to detect and correct variations and irregularities occurring within the medication tablet scope of production. This enables them to conform to regulatory requirements; hence, the quality of the final product is noncompromising, safe, and fulfills the necessary therapeutic functionalities. These measures assist the manufacturers in achieving the required standards of quality, compliance with the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and the standards developed by regulatory agencies.
These quality control measures allow manufacturers to enhance structural and functional performance of their tablets as well as ensuring the ease of use among healthcare specialists and patients.
Testing Tablet Properties for Consistency
Obtaining the properties of tablets should be an attempt to make sure that every single tablet is of the required quality and avails the intended use in the form of therapy. All the qualities as mentioned above can be achieved through such ensuing quality control measures as content uniformity, dissolution, and stability testing: Kingston, Outteridge, and McGee devise strategies to encourage growing competition. These measures assist in detecting and remedying any discrepancies or disparities that happen during the tablet production processes and ensure compliance with the regulations set. By using these methods of ensuring quality, we are able to produce tablets for depression patients, and health professionals are guaranteed their safety and effectiveness.
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the main steps involved in the tablet manufacturing process?
A: The tablet manufacturing process generally involves several manufacturing stages, including the dispensing of ingredients, granulation (wet or dry), blending, tablet compaction, and coating. Each step is crucial to ensure the quality and effectiveness of the pharma tablet.
Q: How does the granulation technique affect the manufacturing of pharma tablets?
A: Granulation is a critical step in the process of making tablets as it improves the flow and compressibility of the tablet ingredients. The wet granulation method is commonly used to achieve a uniform blend, which helps in the consistent delivery of drugs.
Q: What role does the tablet coating machine play in the manufacturing process?
A: The tablet coating machine is used to apply a coating to the tablets, which can enhance the stability of the pharmaceutical tablet, mask the taste, and control the release of the medicine. This coating process is essential for the effective delivery of drugs.
Q: Why is direct compression method preferred in some cases?
A: The direct compression method is preferred for its simplicity and efficiency. It allows for the direct compaction of ingredients without the need for granulation, which is particularly useful for materials that are sensitive to moisture.
Q: How does humidity affect the tablet manufacturing process?
A: Humidity can significantly impact the quality of the pharma tablets. High humidity can cause issues like capping and sticking during tablet compaction, while low humidity can result in brittle tablets. Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity conditions is crucial.
Q: What is the purpose of using calcium phosphate in tablet formulations?
A: Calcium phosphate is commonly used as an excipient in pharmaceutical tablets. It aids in the tablet compaction process, providing necessary bulk and stability to the tablet, and is generally not soluble in water, which helps in controlled drug release.
Q: How are active ingredients and excipients mixed in tablet manufacturing?
A: Active ingredients and excipients are mixed using specialized mixing equipment to ensure a uniform blend. This step, called the mixing or blending step, is critical to ensure that each batch of tablets contains the precise amount of active ingredient for effective drug delivery.
Q: What challenges are faced during the tablet coating process?
A: The tablet coating process can be challenging due to factors like uneven coating caused by improper mixing or spraying techniques. Consistent coating is essential for the effective delivery of drugs and to maintain the integrity of the pharmaceutical tablet.
Q: Why is the sieving step important in tablet manufacturing?
A: The sieving step is crucial for removing oversized particles and ensuring uniform granule size. This helps in achieving consistent tablet compaction and prevents issues like capping or uneven drug distribution in the final batch of tablets.









