Laser-cutting machines have changed home fabrication from manual procedures to an accurate and multifunctional system previously available to industries. Focused laser beams delete and engrave with precision, making these machines important for hobbyists, makers, and small business owners. This guide looks to help novices grasp the fundamentals of laser cutting, which touch on its components, how the technology operates, and real-life use-cases. If you want to design detailed artwork, manufacture specialized prototypes, or launch a cottage industry, you should appreciate what laser cutting machines can do and their requirements. This article aims to remove the uncertainties surrounding a new technology while detailing the key factors to consider when using this equipment. This article is a reliable resource for anyone looking into home fabrication.
What is a laser cutter and how does it work?
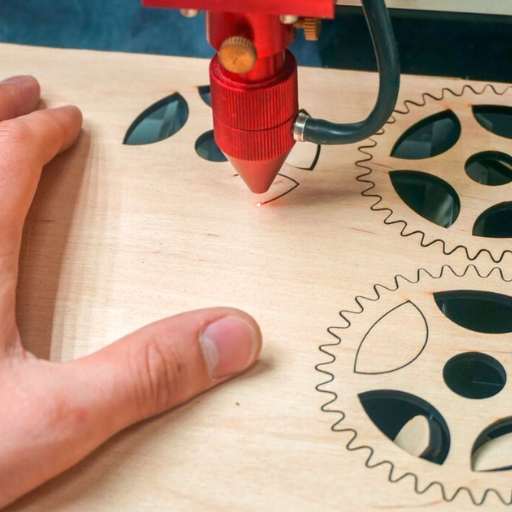

A laser cutter is a precision tool that can engrave, cut, or etch various materials through a revolving beam of light. The laser cutting process requires focusing the laser beam towards the material, which is then vaporized, melted, or heated for cutting. Laser cutting is computer-controlled, meaning anything from simple shapes to detailed images can be cut. The machine uses the laser source combined with mirrors and lenses, plus the motion control system, to process materials accurately. Different materials have other limitations on the type of laser, power, and speed to be set. Hence it can be used for a variety of industries and purposes.
Understanding the basics of laser cutting technology
In its most basic form, laser cutting technology involves firing a laser beam at a particular material to cut or engrave it with extreme precision. The laser emits very high amounts of heat that melt, burn, or vaporize the material’s surface. The laser is controlled via motion control systems, usually powered by computer aided design (CAD) software, which dictate the laser’s path and allow for the formation of complex patterns and shapes. Cutting speed, type of material, and laser power are parameters that need to be set in order to achieve the desired results. This makes using the technology on metals, plastics, wood, textiles, and many other materials possible.
Different types of lasers: CO2, diode, and fiber
Reflective materials, particularly metals, pose a challenge for CO2 lasers, which are regarded as the most effective for cutting nonmetallic materials such as wooden and acrylic objects, paper, and some types of plastic. CO2 lasers have a longer wavelength—around 10.6 micrometers—that is good for absorbing and processing organic materials. Compared to other laser types, CO2 lasers stand out with their efficient power range, which typically starts from 20W and goes as high as 400W, providing deeper and faster cuts.
Diode lasers have low energy consumption and sport a small size. They are ideal for carrying out precision engraving, marking, and cutting thin materials with power levels that range from 1 to 15 watts, making them best suited for applications that require lower power. In addition to their portability, they are relatively easy to make and are great for fine detailing. But just like fiber lasers, their power is minimal; making them unsuitable for working with thicker or harder materials. Their wavelengths also operate between 800 and 980 nanometers.
The most prominent feature of fiber lasers is their versatility, which gives them a primary use for cutting metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and even brass. This is thanks to their high energy density and a wavelength range of around 1.06 micrometers. The excellent absorption of metals combined with fast cutting allows for efficient results. In industrial-scale scenarios, fiber lasers commonly range from 150 watts to several kilowatts. They are solid-state designed, which diversified their lifespan while lowering required maintenance. However, higher upfront costs are a drawback compared to other laser types.
Fundamental Parts of a Laser Cutting Machine
Laser Resonator
The laser resonator is the heart of the system producing the laser beam. It does this by exciting the losing medium in the laser, gas in CO2 lasers or fiber in fiber lasers, to get a coherent light wave. The power and quality of the beam are greatly influenced by how effective the resonator is.
Beam Delivery System
The laser beam produced is sent to the cutting head via a beam delivery system. This system normally contains mirrors or fiber optics with low transmission loss for accurate beam delivery. The accuracy of the beam delivery is of the utmost importance for fine cuts and precision work.
Cutting Head
The cutting head contains the focusing lenses and the nozzle, the most essential parts. The lenses concentrate the beam into a small, high energy spot and the nozzle feeds gas (oxygen or nitrogen) that also aids in cooling the actual area to minimize deformation.
Motion Control System
The motion control system lets the laser-operated head or workpiece move within controlled limits to ensure that the laser cuts in the desired path. This is usually done using CNC technology, which is usually automated and accurate.
Assist Gas Supply
The assist gas supply unit provides the gas needed to cool, oxidize, or remove molten materials during cutting. The gas type depends on the material and its use, but it mostly comes in the form of oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air.
Power Supply Unit
At the same time, the power supply unit must also be reliable. It has to power the laser resonator along with its other electronics. It does so by ensuring that a stable energy source is present, which can directly affect performance and efficiency.
Cooling System
Like all laser cutting systems, it generates considerable operational heat. A cooling system, like water chillers, is incorporated to suppress this heat to safe operating levels, which prevents other sensitive components from being harmed.
Controller and Software
The controller, along with special software, is responsible for the entire operation of the laser cutting machine. It programs motion control, power control, and synchronization of all components of the laser cutter for accurate and effective cutting.
Shielding Encapsulations and Safety Mechanisms
The Shielding encapsulation is built to protect the user from dangerous laser radiation and other threats. Along with the structure, safety features like interlocks and emergency stop buttons are included to ensure the machine’s safe functioning and regulatory compliance.
Which laser cutter is best for beginners?
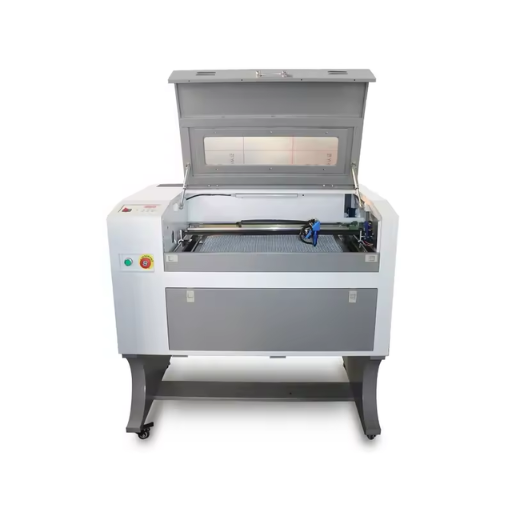

When selecting a laser cutter for beginners, focusing on machines that prioritize ease of use, affordability, and versatility is essential. Key considerations include a user-friendly interface, straightforward software integration, and comprehensive safety features. Additionally, opting for a model with lower wattage is often sufficient for beginners, as it can handle materials like wood, acrylic, and paper without requiring extensive experience. Finally, reliable customer support and accessible maintenance resources can significantly enhance the learning experience, ensuring a smooth introduction to laser cutting.
Desktop laser engravers for home use
Desktop laser engravers for home use should prioritize a compact design, ease of operation, and compatibility with various materials. These devices are tailored for small-scale projects, including engraving wood, acrylic, leather, and even glass, making them suitable for personal or creative applications. Features such as user-friendly software and safety mechanisms enhance their usability for beginners and hobbyists. Additionally, models that offer efficient engraving speeds and adjustable power settings ensure adaptability to diverse tasks while preserving precision and detail in the final outputs. A well-rounded machine combines reliability, affordability, and manageable size for seamless integration into home environments.
Elements to examine while buying your first laser cutter
When selecting your first laser cutter, several important aspects must be considered to guarantee that it fulfills your requirements and works appropriately. First, consider the type of laser the machine uses, be it CO2, fiber, or diode. CO2 lasers work well when cutting and engraving a variety of non-metal materials, while fiber lasers work best with metals. Diode lasers are compact and good for basic engraving. The power of the laser, which is gauged in watts, determines the machine’s capability, and for first-time users, models rated at 40-60W are optimal for most small and medium tasks.
Secondly, evaluate the work space according to the size tag of your projected works. Basic models usually come with a workspace of roughly 12’ x 8’, while higher-end models come with larger work areas. Higher-end models offer more versatility. The power of the Won laser is also important. The higher the DPI setting, like 1000 or more, the sharper the engraving result.
Also, safety elements like the enclosed structure, ventilation, and emergency stop buttons are mandatory, especially for domestic settings. Connectivity is another factor to consider, as many modern laser cutters facilitate the use of USB, Wi-Fi, or other software integrations to make their usage easier. Lastly, look for the availability of customer support and spare parts and user forums, which are essential resources for problem resolution and maintenance. Adjusting these criteria with your budget will lead you towards the most appropriate option depending on your needs.
What materials can I cut and engrave with a home laser cutter?

At home, laser cutters can perform engraving and cutting on a wide variety of materials like wood, acrylic, plastics, paper, textiles, metals and leather. Powerful industrial machines are required to cut metal however some laser cutters can engrave coated metal. Textiles such as leather can be engraved and cut for custom accessories. Paper and cardstock are ideal for intricate cuts on crafts and invitations and acrylic can be used for signage or decorations. Always consult the laser cutter manual to ensure compatibility and optimal results.
Effective materials for laser cutting: wood and acrylic, among others.
Wood is the most flexible material you can work with as an engraver or laser cutter, helping you create detailed functional and decorative pieces. Another top pick is Acrylic, which is used heavily for cutting signs, ornaments, and models because of its clean edges. Paper, cardstock, and leather are other materials widely utilized for custom designs, accessories, and many unique projects. Remember, you must check that your specific material matches the laser cutter’s settings to get the required precision and quality.
Materials that should not be used in laser cutting
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): When cutting PVC, the toxic chlorine gas released is hazardous to health and will corrode the internal parts of the laser cutter.
- Polycarbonate: Most laser systems do not cut polycarbonate well, and the cutting process itself can create dangerous fumes that produce poor quality.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Cutting ABS will create a lot of soot and bad smells while generating rough edges and cuts overall.
- Fiberglass: This composite material consists of glass fibers and epoxy resins. When processed, it can emit harmful fumes and rapidly ruin the optics of the laser cutter.
- Coated Carbon Fibers: Coated carbon fibers, like fiberglass, can emit toxic fumes, and the material’s abrasive nature can also damage the machine’s components.
- Metal (without compatible equipment): Trying to cut any form of metal without having the right laser cutter is ineffective and could damage the cutter if the device was not designed for laser metal cutting.
Creative Ideas to Use With Your Laser Cutter
Laser cutters can be utilized for many different creative projects, including designing personalized home décor pieces like wall art, clocks, coasters, jewelry, and more. For example, jewelry makers can craft intricate earrings, necklaces, and bracelets from wood, acrylic, or other compatible materials. Tumblers, phone cases, and cutting boards can be custom engraved, and used as a gift or for branding purposes. In addition, many details for architectural models, product prototypes, or hobbyist sculptures can be cut out with a laser cutter. The degree of accuracy and detail possible in each piece makes it an unparalleled technology in model building. These projects, adequately set up in the right design software, show the full creativity possible with a laser cutter.
How do I set up and use a laser cutter at home?
There is special software needed depending on the specific system being used. The capability of the system in both cutting and engraving should be checked before commencing. Blank materials/ substrates can be used but care should be taken to ensure that no chemicals are used that would create harmful fume sides and be hazardous to health. Make sure the space where the laser cutter will be set up is easily accessible to maximize airflow. Fumes can easily be a problem so selecting an area that is spacious along with possessing low furniture is essential. This will help guarantee that almost all toxic fumes are cleared. The further the laser cutter is set from the ground, the better. It should not be more than 5 feet above as ventilation will not be optimal. The entire process, from setup to the cutting process, requires supervision to ensure everything goes according to plan. Similarly, the cutting device should be lined up to the appropriate height allowing the setting of power, speed, and other attributes. A test design should be uploaded before commencing work to ensure everything is working perfectly. Safety goggles, alongside other protection gear, should be worn as well.
Critical safety measures to take regarding laser cutting
In every laser cutter’s functionality, safety is key and should be taken into consideration in every step of the whole process. Always ensure that the room has sufficient ventilation for the toxic fumes emitted and try to utilize materials that have already been approved to be used with lasers. Never walk away from the machine while it is in use and ensure that you check for any anomalies. Furthermore, proper personal protective equipment needs to be worn; specifically, laser safety glasses should be worn, and their wavelength should match the cutter’s. Fire extinguishers should always be readily accessible in an emergency, and remember to check for any materials that could start a fire. Ensure that routine checks and servicing of the device are done, and clean its optical parts to ensure it continues to function correctly and cuts accurately. Always follow the safety guidelines within the user guide given by the device maker.
Comprehensive instructions on cutting with a laser machine
- As a starting point, do ensure that the area where the work is to be done is clean and is free from obstructions and flammable materials.
- Switch on the laser cutter and allow it to initialize per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Place the item to be cut within the device’s working section and secure it appropriately so precision is attained while cutting.
- Design files should be sent to the device’s software along with the rest of the parameters such as speed, power, and focus in relevance to what materials require to be set values.
- Before starting the complete task, do a test cut or focus adjustment to check the alignment and cutting accuracy to ensure the results.
- Cutting can begin. At the same time, the user should be on the lookout for any abnormalities or problems with the machine.
- After the cutting is done, cool the machine down before taking out the workpiece and undertaking a post-operation inspection.
Maintaining, servicing and troubleshooting your laser cutter
The effectiveness and life of the laser cutter can be elongated with proper maintenance. To keep the power and accuracy of the laser high, clean the lenses and mirrors from dirt or residue regularly. Adjust or change filters in the exhaust system from time to time for optimal ventilation. Belts, rails, and screws should be clipped, and realigned to address misalignment or wear. For malfunctions, check if the optics is aligned and undamaged. If the cuts are uneven, the focus should be recalibrated or the material’s position should be assessed. It is best to always refer to the user manual for the specific issues and diagnostics for your model.
What software do I need for laser cutting and engraving?
The tools needed for laser engraving and cutting involves two programs: one for designing and the second for controlling the machine. Business design programs like Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, and AutoCAD are equipped with tools for creating and modifying vector graphics and technical drawings. After the designs are done, they require specific control software, such as LightBurn or RDWorks, to manage the laser cutter. Users can define parameters such as cutting speed, laser power, and engraving depth. Ensure the software is compatible with the file types used in your laser cutter, which usually are DXF, AI, or SVG. The design and control software, as well as the laser cutter, need to be compatible to achieve the highest level of accuracy and efficiency.
Best design software for styling laser cutting projects
For laser cutting projects, Adobe Illustrator, a vector graphic software with an easy-to-use interface, is frequently utilized. CorelDRAW, which has complete design capabilities at a reasonable price for small businesses, and AutoCAD, which is highly precise and good for technical designs, are also frequently utilized. All three programs allow saving in DXF, AI, and SVG, which are acceptable by nearly all laser-cutting machines. Which program to use is determined by the intricacy of the project and individual design requirements.
Understanding laser cutter control software
A laser cutter control software interprets your design files and formulates directions for the hardware to fulfill, whether it be cuts or engravings. For effective results, most software obtains the provision to set essential details such as focus height, cutting speed, and power. For instance, the cutting speed is determined by the material used as well as the power of the laser; thus it can range between 10-500 mm/s. The focus power is also set as a percentage of the maximum laser power, usually set at a depth of 10%-100% of the maximum. Some software has built-in libraries that predefine parameters for certain materials along with features that optimize efficiency, reducing the required time for processing. The most significant degree of control efficiency is achieved when it corresponds to the hardware performance and user targets.
Free vs. Paid Software Choices for Newbies
Beginners seem to enjoy free options like LaserGRBL because of how simple it is to use and its accessibility. However, it is usually limited with the features it provides like presets for specific materials and advanced optimizing tools. In contrast, LightBurn offers more options and features with design tools, multi-layer editing, and workflow automation. These software solutions come with customer support and regular updates making it easier for users looking for a comprehensive solution. New users will significantly benefit by starting with free options to complex piece software as their requirements grow.
What are the limitations and challenges of home laser cutting?

While home laser cutting is extremely versatile, it does have some limitations. One of the main problems is the equipment cost which can be worrying especially for advanced machines. The cutting process also produces fumes and particulates that must be adequately vented or filtered to meet safety regulations. There are also material limitations, since some metals and PVC cannot be effectively and safely cut. The bounds of the machine’s working area may limit the size of the projects, and maintaining a certain level of precise measurements may as well depend on the level of upkeep. Finally, for a novice learner, the techniques and software learning can be very complicated and require much time and effort to master.
The Effect of Laser Power on Cutting Accuracy and Materials
As is evident from information already stated, lasers have different power levels, which directly correlates with the materials and projects that can be undertaken.The capabilities of a home laser cutter, for example, its ability to cut achieves depend on the laser’s power. A home setup typically has access to 40W-150W, and the higher the wattage, the denser and thicker the material that can be cut. A 40W CO2 laser can cut acrylic or wood up to 1/4 inch thick. Meanwhile, depending on the material, a 100W laser can handle thicknesses of up to 3/4 inch or more. Additionally, precision in cutting gets impacted too, lower-powered precision lasers may need several passes and this greatly ruins the overall edge quality due to heat buildup.
The property of materials and their interaction with the zoomed-in power of a laser varies with a lot of conditions.A good example is metals that have better thermal conductivity and often require nitrogen or oxygen having assistance to make clean cuts, which may not be feasible with low-power lasers. Non-metals, on the other hand, do not require as much assistance. However, too much power will lead to charring and warping. Accurate calibration of power settings ensures optimal performance. In addition, combining high power output with slow speed adjustments causes under-processing of the material and, for the opposite, over-processing. High power coupled with fast speed is ideal.
Typical Problems Resulting from Starting Issues in Laser Cutting
One of the cutting issues a beginner in laser cutting faces is setting the focus. Cutting quality precision will not be achieved if the cutting focus is not set properly. There is also the problem with setting the right power and speed for cutting as it may result in unclean cutting of the material, over charring, or loss of material through cutting. Furthermore, lack of understanding regarding material damage can equally harm both the material and the laser machine. Overlooking maintenance basics like cleaning, aligning lenses, or even changing filters disables proper cutting performance after some time, which, ironically, tends to be more harmful to beginners.
Moving From An At Home Laser Cutter To A Professional Machine
Moving from a home laser cutter to a professional machine is warranted when the workload exceeds what can be achieved with the home model. Advanced users will need sophisticated tools to support faster processing times and meet higher output requirements on advanced materials that are useless to smaller machines. Professional cutters excel not just in wattage and computer software—their added durability and bigger working areas make them superior for the industrial setting and scaling operations.
Reference sources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between CO2 laser cutters and diode laser engravers?
A: CO2 laser cutters are generally more powerful and versatile, capable of cutting and engraving a wider range of materials like wood, acrylic, and leather. Diode laser engravers are typically less powerful but more compact and suitable for home use, primarily for engraving and light cutting on softer materials. CO2 lasers use a gas-filled tube, while diode lasers use semiconductor technology.
Q: What materials can be cut or engraved with a laser cutting machine?
A: Laser cutting machines can work with various materials depending on the type of laser. Common materials include wood, acrylic, leather, paper, cardboard, and some fabrics. CO2 lasers can cut thicker materials, while diode lasers are better for engraving and cutting thinner materials. It’s important to note that some materials, like PVC, should never be used due to toxic fumes.
Q: What safety precautions should I take when using a laser cutting machine at home?
A: Safety is crucial when operating a laser cutter. Always use the machine in a well-ventilated area or with proper ventilation systems. Wear safety goggles designed for the specific wavelength of your laser. Never leave the machine unattended while operating. Use fire-resistant materials around your work area, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby. For CO2 lasers and more powerful machines, consider using an enclosed laser system for added safety.
Q: How do I choose the best laser cutter for my home projects?
A: To choose the best laser cutter for home use, consider factors like the types of projects you’ll be doing, the materials you’ll be working with, and your budget. For beginners, a diode laser engraver might be sufficient for small projects and engraving. If you need more power and versatility, a CO2 laser cutter might be a better choice. Consider the work area size, power output, and software compatibility.
Q: What is the difference between laser engraving and laser cutting?
A: Laser engraving involves using a laser beam to create marks or designs on the surface of a material, typically by vaporizing or discoloring the top layer. Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses a more powerful laser beam to cut completely through the material. Many laser machines can perform both functions, with the difference lying in the power settings and focus of the laser beam. Engraving is generally shallower and used for decorative purposes, while cutting is used to create shapes or parts from the material.
Q: Can laser cutting machines be used for small business or craft projects?
A: Yes, laser cutting machines are excellent tools for small businesses and craft projects. They can be used to create custom products like personalized gifts, jewelry, signage, and decorative items. Many craft enthusiasts and small business owners use laser cutters to produce unique items for sale on platforms. The versatility of these machines allows for a wide range of applications, from engraving names on products to cutting intricate designs for crafts.
Q: What maintenance is required for a home laser cutting machine?
A: Regular maintenance is important for keeping your laser cutting machine in good condition. This typically includes cleaning the lens and mirrors, aligning the laser beam, lubricating moving parts, and checking for any wear or damage. The frequency of maintenance depends on usage, but generally, a thorough cleaning should be done every few weeks or after extensive use. It’s also important to keep the work area clean and free of debris. For CO2 lasers, you may need to periodically refill or replace the laser tube.









