In the world of precise using materials, CNC cutting and laser cutting exemplify the most evolved and utilized technologies today. Each technique has its merits and features, making it appropriate for use in different fields, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and even in custom fabrication. In this article, these two cutting technologies will be compared in detail concerning their operational principles, strengths, limitations, and practical use. Readers ought to understand the differences and applications of CNC and laser cutting because this understanding helps one make the right choice depending on the project needs.
What are the fundamental differences between CNC cutting and laser cutting?

CNC cutting involves using a powerful laser to cut through highly precise materials. The materials used to cut CNC can be metal, wood, plastic or some other material that needs to be precisely cut. The primary component of the cutting machine is a high-powered laser that can melt, burn, or vaporize the material. It is very useful when cutting delicate structures. Even though laser cutting is much more precise, CNC machines are better when it comes to thicker materials or parts with a lot of material that needs to be cut off. Each technique serves its purpose based on the type of materials that need to be cut and the project’s requirements.
How does the cutting process differ for CNC and laser cutting?
While programming paths for the desired output shape, the cutting CNC relies on contact between the tool and the material. This technique works extremely well with thicker materials, allowing for significant material removal. Unlike this method, laser cutting focuses a high energy laser beam on the material. This method thermally processes the material, allowing smooth, non-contact cutting. This non-contact technique allows for the cutting of thinner materials and any other intricate shapes. The primary difference between the two methods is that one uses mechanical force while the other uses thermal energy.
What types of materials can be cut using each method?
CNC cutting can be used for a wide range of materials such as metals like aluminum, brass and steel, various plastics like acrylic, polycarbonate, and even wood. This method is exceptionally beneficial for materials with greater densities and thicknesses because of its greater removal rate. Various technical information such as material hardness, feed rate, tool speed, and cut material quality require parameters set to aid cutting efficiency.
Conversely, laser cutting is superior with thinner materials and is able to cut metals such as stainless steel and titanium, non-metals like glass, ceramics, and acrylic, as well as layered composites. Its precision can be fine-tuned by adjusting parameters such as laser power, beam focus, material thickness, and cutting speed. For example, higher settings are needed in cutting power for thicker materials while lower settings are more appropriate for delicate materials to ensure clean edges. The capacity of each method’s material is deeply connected to the physical or thermal attributes of the cutting process.
What are the differences in speeds when comparing CNC and Laser cutting?
As laser cutting and CNC machining, it is apparent that both methods have differing speeds due to the approach or manner in which their tasks are executed. Unlike laser cutting which has higher speeds because of its focused energy and non-contact nature, CNC cutting has a variety of speeds regarding the machine configuration, material, and even the tools. For example, using saws made from steel will require someone to lower the spindle speeds and feed rates between 30 to 200 surface feet per minute (SFM). Supplementing this, CNC machines that cut thin pieces of metals such as aluminum or stainless steel are easily used by lasers which can achieve up to 500 inches per minute (IPM). Unlike CNC, industrial-piece laser systems will pour 1000-6000 watts of power for oxidation or fusion cutting while considering the material’s thickness and the gas pressure.
Regardless of the benefits that laser cutting presents by speeding through thin materials, CNC outshines when using dense or thicker materials due to the decreased speeds. The selection between the two approaches comes down to the composition of the material, how thick it is, and the desired finesse.
Which cutting method offers better precision and accuracy?

In this modern age, laser cutting is one of the most precise methods, as it can achieve tolerances as precise as +/- 0.003 inches. When focusing on an area, CNC machining can also achieve a similar level of precision, but it usually requires an entirely controlled environment. On the other hand, CNC machining is very effective when it is working on thick or hard materials, because the mechanical tool ensures proper dimensional control. Depending on the machining needs, its type and thickness, the choice of which one to go for can be decided. At the same time one needs to understand that laser cutting is much more effective when dealing with thinner materials and more complex high precision designs, compared to CNC machining.
The Intricacies of Precision Levels in CNC Cutting
The level of detail that can be achieved in CNC cutting usually depends on the individual processes and tools used. Normally, these tools can provide tolerances between +/- 0.001 inches to +/- 0.005 inches. Other factors also determine accuracy, such as the kind of material being cut, the speed of the spindle, and the quality of the cutting tool. When working with softer metals and plastics, much tighter tolerances like the +/- 0.001 inch standard can be achieved, however, harder materials tend to limit how accurate a cut can be. Moreover, staggering technologies such as three-dimensional tool pathing and high-resolution controllers greatly increase the accuracy of CNC operations, improving repeatability for multi-dimensional tasks.
How does precision cutting technology benefit accuracy?
Laser cutting technology employs a high-powered, shining laser beam to cut with a high degree of control and minimal thermal distortion. This technique affords even the most delicate designs exceptional detailing and sharp edges since the width of the laser beam is very small. Moreover, by taking the physical material out of the equation, laser cutting eliminates the chance of mechanical distortion which compromises cleanliness and accuracy. In addition, modern day laser systems use sophisticated software to adjust cutting speed, intensity, and depth, which increases the repeatability and quality of cuts made in different materials.
What are the possible variables that dictate the accuracy for each cutting method?
- Machine Calibration: Systems should be calibrated regularly and accurately to ensure the cutter or laser works within tolerances. Mechanical parts misaligned or worn out can drastically lower accuracy.
- Material Properties: The type and thickness of the material being processed is another aspect that impacts the cutting accuracy. Softer and more ductile materials can deform easily, whereas harder materials need more accurate energy control to prevent the piece from being overcut or damaged.
- Tool Quality: When using mechanical cutting procedures like milling or plasma cutting, the condition and sharpness of the tool are of the utmost importance. A worn-out tool can cause unclean cuts and uneven edges.
- Cutting Speed: The speed with which cutting is done influences the accuracy. Elevated speeds may cause cuts to reduce precision because vibrations or incomplete machining can affect the quality of the cut.
- Thermal Effects: When using methods such as plasma or laser cutting, the heat produced can cause the material to thermally expand or even distort, greatly reducing the quality of the cut.
- Software Parameters: The calibration of cutting software, including optimization parameters for path, type of movement, and speed, determines the accuracy of cutting. Errors in parameter entry letters, such as programming, can produce inaccurate outputs.
- Environmental Factors: Changes in the surrounding environment, such as temperature, humidity, vapor thickness, and barometric pressure, can lightly affect the results of some cutting processes, especially those dependent on gas or sensitive to heat energy.
- Operator Skill: The operator’s experience and concentration are important. An experienced set operator can foresee possible difficulties in a set period of time and make changes in the machine or work piece to maintain the measuring accuracy.
How do CNC and laser cutting compare in terms of versatility and applications?
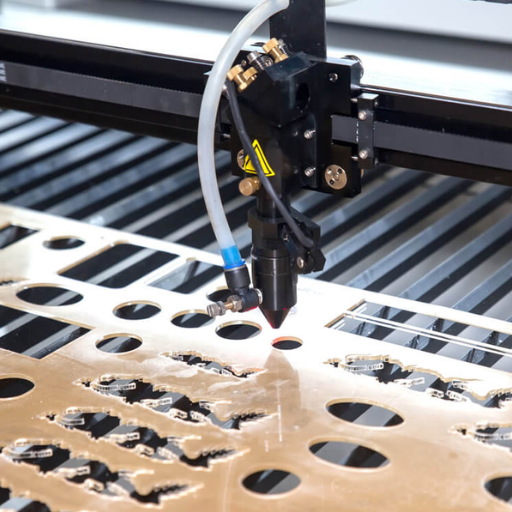
CNC cutting and laser cutting have their own specific strengths regarding versatility and applications depending on the material and level of precision required. CNC cutting serves a greater scope of materials like metals, plastics, woods, and composites for cutting, drilling, milling, and even more complex 3D shaping. It is best suited for processes that require multifunctional parts and structural strength, like components manufacturing, furniture production, or prototypes. Laser cutting, however, achieves unmatched finesse and highly detailed edges, especially on thin metals, plastic, and fabric, which are important for engraving or exact detailed laser cutting. Although detail-oriented tasks are best done quickly and efficiently using laser cutting, CNC cutting is ideal for heavy-duty tasks or intricate shapes.
Which industries uses CNC Cutting techniques the most?
CNC cutting is widely utilized in the manufacturing and construction industries due to the requirements of high durability and accuracy. Aerospace brings a lot of CNC machining business because metals and composite parts with complex shapes and high performance metrics have to be made. The automotive sector utilizes CNC cutting for critical component manufacturing, such as engine parts, transmission cases, and custom prototypes. CNC machining is also used in medicine for instruments and implants where high precision and material properties must be preserved. Construction, electronic goods manufacturing, and many others also use CNC cutting because of its exceptional versatility, accuracy and repeatability. All industries whose products require cutting components benefit from this technology.
What parts of the world use laser cutting machine and why?
- Manufacturing and Fabrication: Laser cutting is one of the primary processes in the manufacturing industry, where crafts are made, metal sheets are cut, and other engineered items are produced with minimum material utilization. It is highly suitable for repetitive processes as well as those that require precision.
- Automotive Industry: This technology is used extensively for cutting and engraving components such as gears, airbags, and vehicle interiors. It has an edge over many other technologies in dealing with different alloys of metals and even other non metallic materials in the auto industry.
- Electronics: In the electronics industry, surgical laser cutting is employed to manufacture highly delicate components such as circuit boards, microchips, and consumer electronics parts. Additionally, it does not touch the surrounding objects which avoids sensitive material.
- Jewelry and Fashion: The fashion industry greatly benefits from laser-cut gifting products by creating minute details on jewelry pieces and intricate designs on leather and cloth. This gives a chance to go wild with creativity without compromising on quality.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry uses laser cutting to produce lightweight components from specialized materials like titanium and composites while maintaining great durability. Its merits of its ability to achieve great accuracy has earned it much appreciation amongst those in the aerospace industry.
- Medical Devices: Like in other applications, the medical industry has greatly benefitted from laser cutting in surgical tools, implants, and stents, in which precision, accuracy, and biocompatibility are crucial.
- Signage and Advertising: The advertisement and marketing industry uses laser cutting to produce custom, elaborate signs, logos, and design elements that need to be presented in great detail.
- Architecture and Construction: Builders and architects produce detailed models and complex façade design cuts, along with the details required in modern architecture, while utilizing advanced metals, glass, and even composite panels.
Why can CAD methods be employed in the prototyping phase and CNC laser cutting can handle small production runs?
Laser cutting and CNC machining methods can definitely be used for prototyping and production. Due to its unparalleled speed and accuracy, small business manufacturing uses laser cutting to produce conclusive designs. Also, CNC machining can produce a wide variety of materials and pro type parts with high accuracy. These processes can be selected based on material, design complexity, and finishing requirements, as they are flexible and can be applied to specific projects.
What are the cost considerations when choosing between CNC and laser cutting?

Multiple factors need to be investigated regarding the cost considerations of laser cutting versus CNC machining. For precision work with thin materials, laser cutting is usually more economical as the setup time is much lower and the cutting is faster. However, its effectiveness diminishes with thicker materials, which may add to the cost. On the contrary, CNC is mostly more expensive and more time-consuming due to the high setup costs and low efficiency rates. CNC is, however, much better with thick and complex materials. Other costs that include maintenance, tooling, and material waste also differ. Generally speaking, laser machines tend to waste less material which helps lower costs. Overall, the best solution depends on the specific needs of each project such as the material, design toll, and production volume.
How do CNC machines and Laser cutting machines differ in investment cost?
When examining the investment costs of CNC machines and laser cutters, a range of specific elements must be considered. CNC machines almost always have a higher investment capital cost that frequently surpasses $15,000 and can go as high as a staggering $100,000! The figures depend on the machine’s size and number of axes, along with the intended application. Most industries find it worth investing in because of their wide range of complex geometries along with host of materials. Laser Cutters, however, take the cake as their investment costs vary between 10,000 to 250,000, depending on the same criteria as the previously mentioned CT machines. Not unlike our CNC principals, cheaper variants such as CO2 cutters come at the lowest and standardized cutting bed size, and laser systems such as fiber and crystal lasers are standard among the overpriced options. Although smaller system laser cutters have cheaper initial investment costs, the industrial high-powered variants are out of control regarding pricing, making them unfathomably more expensive than CNC machines. Economical viability differs based on operational needs and intended use, which is programmable depending on the scale of desired production.
What are the ongoing operational costs for each cutting method?
In the cost analysis of CNC machines, I include costs of tooling, maintenance, energy, and software updates that are performed occasionally. The tool life is a major factor in determining the cost, and so is the maintenance, which consists of the machine’s lubrication, calibration, and replacement parts. Laser cutters tend to incur higher costs from electric consumption, cooling, and maintenance of the laser tube or source. Comparison of CO2 and fiber laser shows that the former has greater need for servicing while the latter’s maintenance is usually minimal. Operational costs are however dependent on the level of intensity, type of system, and maintenance performed.
How does material waste differ between CNC and laser cutting?
Due to differences in cutting processes, a measure of waste poundage between the two methods, CNC and laser cutting, differ significantly. My experience shows that laser cutting wastes raw materials like CNC machining. However, in terms of poorly shredded material characterized as chips or shavings, CNC cutting seems to have the upper hand. In addition, laser cutting is less of a wasteful process because when cutting with a laser beam, the very thin width (kerf) of the material that is shaved off is minimum. It is worth noting that aside from the type of material, waste levels for both methods are determined by the complexity of the design to be cut.
What are the limitations and challenges of CNC cutting vs laser cutting?

CNC cutting and laser cutting face unique challenges and limitations. CNC cutting has a broad range of uses. However, it does not achieve the fine detail lasers can, particularly in small-scale and meticulous projects. Furthermore, CNC machines tend to be slower with complex geometries, needing more material to be removed and often producing waste. Maintenance is also a pain point.
On the bright side, laser cutting is precise and can cut materials easily. However, the variety of materials it can work on is restricted. Some reflective materials like copper or aluminum could be problematic for laser cutting systems. Thickness is a constraint because heavy duty lasers are not as effective as CNC machines for cutting thick materials. Additionally, laser systems are costlier upfront and they need good ventilation or proper filtration to remove fumes during the cutting process. Both systems require skillful operators.
What are the thickness restrictions for laser cutting?
The thickness restrictions for laser cutting vary based on the material type as well as the power of the laser being used. Metals work with CO2 lasers that handle stainless steel and aluminum at 0.25 inches, and fiber lasers utilize advanced systems to cut steel up to 1 inch. Non-metals like wood or acrylic can be cut with lasers up to 1 inch thick, although outcome can depend on the density and quality of the material. Increased thickness of the material being cut requires slower cutting speed and increased power from the laser, and there is a tradeoff of reduced edge quality.
How does the complexity of designs affect each cutting method?
The intricacy of the designs influences the efficiency and achievability of the cutting methods. Complex design elements are best handled through laser cutting as it offers minimal material resistance. Sharp corners or densely packed designs may require adjustments, slowing down the overall process. CNC cutting works well with complex shapes, but with an added lack of detail in comparison. It works better with simpler, larger shapes, especially in thicker materials with beneficial routing or milling capabilities.
What maintenance considerations do CNC and laser cutting machines need?
CNC and laser cutting machines require routine maintenance to ensure efficient productivity and an extended life span. In regards to CNC machines, regular servicing that includes cleaning and lubrication with oil of the moving parts such as linear guides, ball screws and bearings must be undertaken. Furthermore, cleaning and properly maintaining the cooling system, spindle motors and other key components in the machine is essential to prevent overheating. For laser cutting machines, the quality of the laser lens and mirrors must be maintained for precision; otherwise, they will become misaligned. Reliable operation is also achieved by routinely cleaning the optic components, checking laser power output and replacing broken nozzles. In addition, both machines experience increased efficiency with periodic updates in the software and firmware. Last but not least, regular diagnosis for underlying disorders is essential to avoid overheads downtime in both CNC and laser cutting systems.
How do environmental impacts compare between CNC and laser cutting?
The effects of each cutting method on the environment differ significantly because of how the procedures are done and how much energy is required. CNC machines have subtractive manufacturing as a technique, allowing the release of more waste material than is necessary. They achieve the desired shape by carving away from a solid block. Although waste can be substantial, much material can be recycled. Unlike Laser cutting, which is more power-hungry because of the high-energy lasers used. Laser cutting also causes greater energy consumption; however, the amount of waste debris produced is smaller. Furthermore, laser cutting can emit fumes or gases, especially when cutting non-metals, which might necessitate appropriate filtering systems to mitigate air pollution. Regarding energy efficiency and waste management approaches, both systems have toiled to improve their reach, thus lessening their effects on the environment.
What are the energy consumption differences?
The differences in energy consumption between CNC and laser cutting are closely linked to their operating mechanisms and power consumption. CNC machines usually consume less energy compared to other systems since their spindle motors and cutting tools do not have extremely high power demands. Their energy usage depends on spindle speed, tool pressure, and cutting depth, typically between standard operations consuming 0.4 kWh and 1.5 kWh.
Laser cutting, although typically faster, uses up much more energy than other methods due to the laser source. CO2 lasers, for instance, may use up anywhere from 6 kWh to 15 kWh depending on the material and its thickness, whereas fiber lasers are much more efficient, using only 2 kWh to 8 kWh. Moreover, laser cutting machines require other systems like cooling units and gas assists, which overall increases energy use compared to CNC. This shows the clash that exists between energy conservation, speed of processing, and the quantity of materials produced.
How do waste products and emissions compare?
When looking at waste products and emissions, CNC cutting produces the most solid waste in the form of metal shavings, which are recyclable. The emissions from these systems are direct but very little, since the main concern is dealing with the coolant and its waste. On the other hand, cutting lasers produces gaseous emissions, which include fumes and other particles, especially from cutting plastics or coated metals. There is a need for environmental filtration and extraction systems to reduce the negative impact of these fumes on the environment. This complicates waste management and emission control for laser cutting operations, thus increasing the cost and making them more challenging.
Which cutting methods provides greater sustainability benefits?
Both methods of cutting, mechanical and manual, possess eco-friendly benefits that depend on their use and setting. Manual cutting does not use electricity or fuel and thus saves energy. However, some large scale operations might be more efficient with mechanical cutting. Mechanical cutting can be done with energy-efficient equipment or renewable power sources in the plants. Achieving the desired level of sustainability in each method highly depends on how operationally effective, material resourceful and what type of energy is used.
Reference sources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the main differences between CNC cutting and laser cutting?
A: The main differences between CNC cutting and laser cutting lie in their cutting methods and applications. CNC cutting uses a physical cutting tool or router to remove material, while laser cutting uses a focused laser beam to cut or engrave materials. CNC cutting is generally better for cutting thicker materials and 3D shaping, while laser cutting excels at precision cutting of thin materials and intricate designs. CNC cutting can handle a wider range of materials, including metals and thick woods, whereas laser cutting is ideal for thin materials like plastics, thin wood, and fabrics.
Q: What types of laser cutters are commonly used in industry?
A: There are several types of laser cutters commonly used in industry, including: 1. CO2 lasers: Ideal for cutting and engraving non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, and fabric. 2. Fiber lasers: Excellent for cutting metals and reflective materials. 3. YAG lasers: Suitable for cutting and engraving metals and some plastics. Each type of laser has its specific applications and advantages, making them suitable for different materials and cutting requirements.
Q: How does using a CNC router differ from using a laser cutter for woodworking?
A: Using a CNC router for woodworking differs from using a laser cutter in several ways. CNC routers use a physical cutting tool to remove material, allowing for deeper cuts and 3D shaping of wood. They can handle thicker materials and create more complex 3D shapes. Laser cutters, on the other hand, use a focused laser beam to burn or vaporize the wood, making them ideal for intricate 2D designs, engravings, and cutting thin plywood. CNC routers generally have a larger kerf (width of cut) compared to the precise, narrow cuts of a laser.
Q: What are the advantages of CNC cutting over laser cutting when working with plywood?
A: When working with plywood, CNC cutting offers several advantages over laser cutting: 1. Ability to cut thicker plywood sheets 2. Capability to create 3D shapes and profiles 3. No burning or charring of the wood edges 4. Better for creating joinery and interlocking parts 5. More suitable for large-scale production However, it’s important to note that laser cutting can provide more intricate designs and cleaner cuts on thin plywood sheets.
Q: How do CNC milling machines compare to laser cutters in terms of precision and speed?
A: CNC milling machines and laser cutters differ in precision and speed depending on the application. Laser cutters generally offer higher precision for intricate 2D designs and can be faster when cutting thin materials. They produce very fine, clean cuts with minimal material waste. CNC milling machines, while slightly less precise for fine details, excel in 3D shaping and can achieve good precision for most applications. They are generally faster when working with thicker materials or when removing large amounts of material. The choice between CNC vs laser often depends on the specific project requirements, material thickness, and desired finish.
Q: What materials can be cut using CNC routers and laser cutters?
A: CNC routers and laser cutters can work with a wide range of materials, but their capabilities differ: CNC routers can cut: – Wood and plywood – Soft and hard metals – Plastics – Foam – Composites Laser cutters can cut: – Thin wood and plywood – Acrylic and other plastics – Fabric and leather – Paper and cardboard – Thin metals (with fiber lasers) The choice of cutting machine depends on the material type, thickness, and desired finish.
Q: What is the environmental impact of CNC cutting compared to laser cutting?
A: The environmental impact of CNC cutting compared to laser cutting varies: CNC cutting: – Produces physical waste (chips, dust) – Requires cutting tools that need replacement – Uses more energy for material removal – May require cooling fluids Laser cutting: – Produces fumes and potentially harmful gases – Requires proper ventilation – Generally creates less physical waste – More energy-efficient for thin materials Both methods have environmental considerations, and the impact can be minimized through proper waste management, ventilation, and energy-efficient practices.
Q: How do CAD software and computer-aided design factor into CNC and laser cutting processes?
A: Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software plays a crucial role in both CNC and laser cutting processes. It allows users to create precise 2D or 3D digital models of the parts to be cut. For CNC cutting, CAD software is used to design the part and generate toolpaths for the cutting tool. In laser cutting, CAD is used to create the 2D designs that the laser will follow. The CAD files are then converted into machine-readable instructions (G-code) that control the movement and operation of the cutting machine. This integration of CAD with cutting technologies enables high precision, repeatability, and the ability to easily modify designs.









